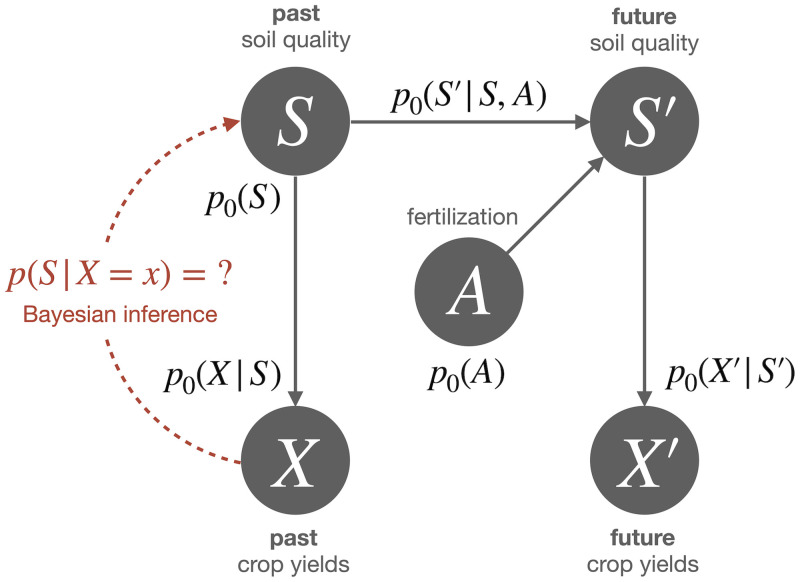
Fig 1. Graphical representation of an exemplary probabilistic model.
The arrows (edges) indicate causal relationships between the random variables (nodes). The full joint distribution p0 over all random variables is sometimes also referred to as a generative model, because it contains the complete knowledge about the random variables and their dependencies and therefore allows to generate simulated data. Such a model could for example be used by a farmer to infer the soil quality S based on the crop yields X through Bayesian inference, which allows to determine a priori unknown distributions such as p(S|X) from the generative model p0 via marginalization and conditionalization.