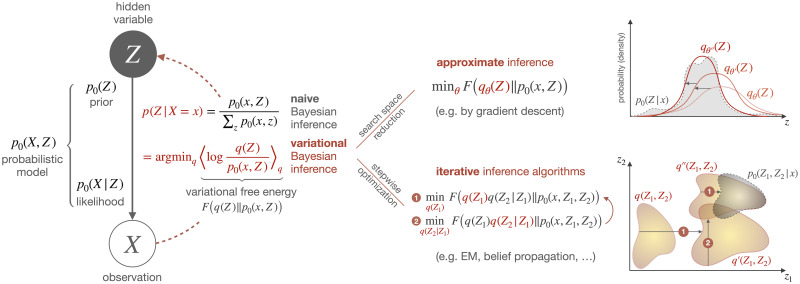
Fig 4. In variational Bayesian inference, the operation of renormalizing the probabilistic model p0 evaluated at an observation X = x (Bayes’ rule), is replaced by an optimization problem.
In practice, this variational representation is often exploited to simplify a given inference problem, either by reducing the seach space of distributions, for example through a restrictive parametrization resulting in approximate inference, or by splitting up the optimization into multiple partial optimization steps that are potentially easier to solve than the original problem but might still converge to the exact solution. These two simplifications can also be combined, for example in the case of mean-field assumptions where the space of distributions is reduced and an efficient iterative inference algorithm is obtained at the same time.