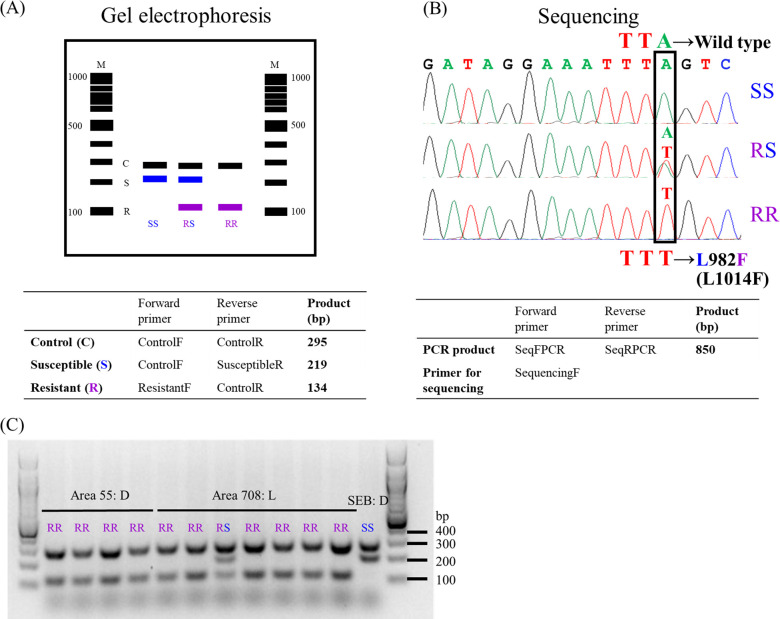
Fig 6. Diagnostic methods for detection of the kdr-like mutation in the voltage-gated sodium channel (Nav).
(A) Schematic of the diagnostic PCR expected products for detecting the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) A (susceptible allele) to T (resistant allele), as resolved on a 1.5% agarose gel. The A to T mutation results in the nonsynonymous L982F mutation in the protein. The ControlF and ControlR primers amplify a 295 bp “control band” product (black) that is expected from all mosquitoes (S1 Fig), the ControlF and SusceptibleR primers amplify a 219 bp “susceptible band” product (blue) only if at least one susceptible allele is present, and the ResistantF and ControlR set amplify a 134 bp “resistant band” product (purple) only if at least one kdr resistant allele is present. (B) The wild type, susceptible codon TTA changes to TTT in the kdr resistant allele (black rectangle) resulting in the sodium channel L982F mutation. Electropherograms of three different genotypes. Top: homozygous susceptible SS (TTA); middle: heterozygous RS (TTA/TTT); and bottom: homozygous resistant mosquitoes RR (TTT) for the L982F mutation. The kdr-like mutation amino acid residue position in the sodium channel of the house fly is shown in parenthesis. (C) Diagnostic PCR results of field collected mosquitoes from areas 55 and 708, and Sebring strain (SEB) mosquitoes from 91.2 m. D, mosquitoes were dead after Permanone® treatment; L, alive after Permanone® treatment.