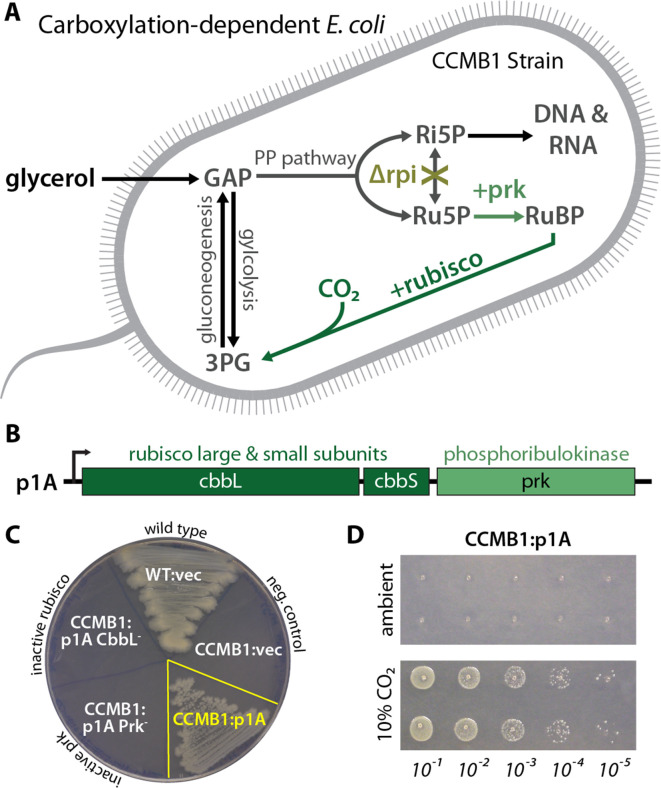
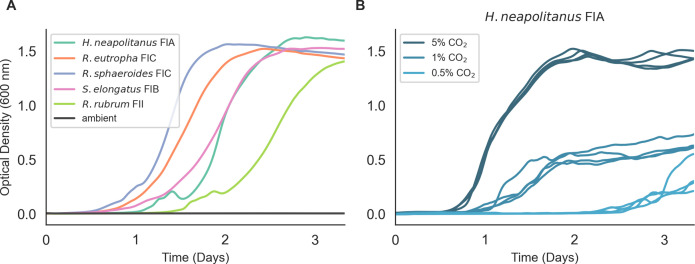
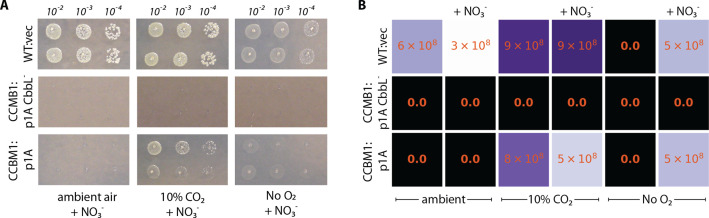
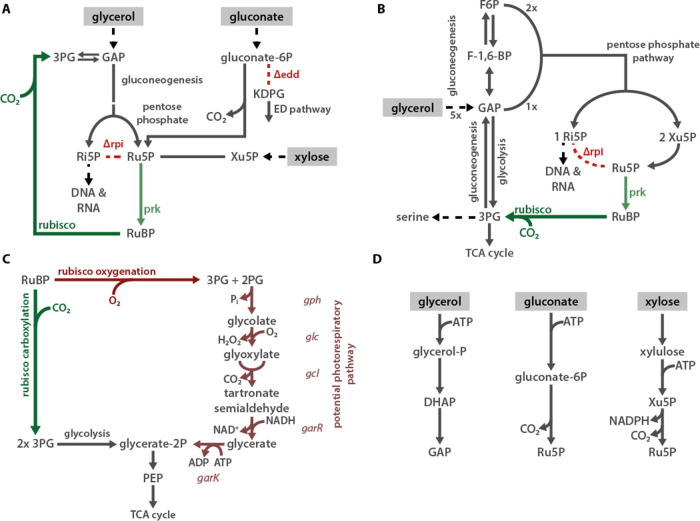
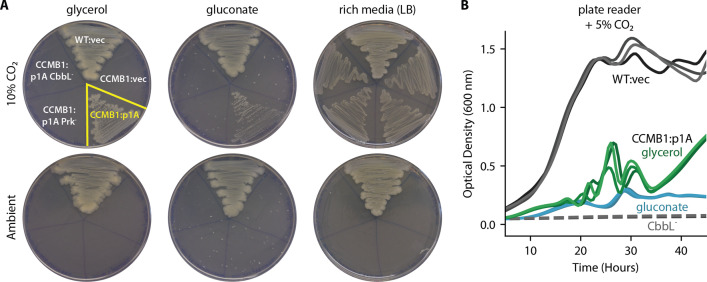
Figure 2. CCMB1 depends on rubisco carboxylation for growth on glycerol.
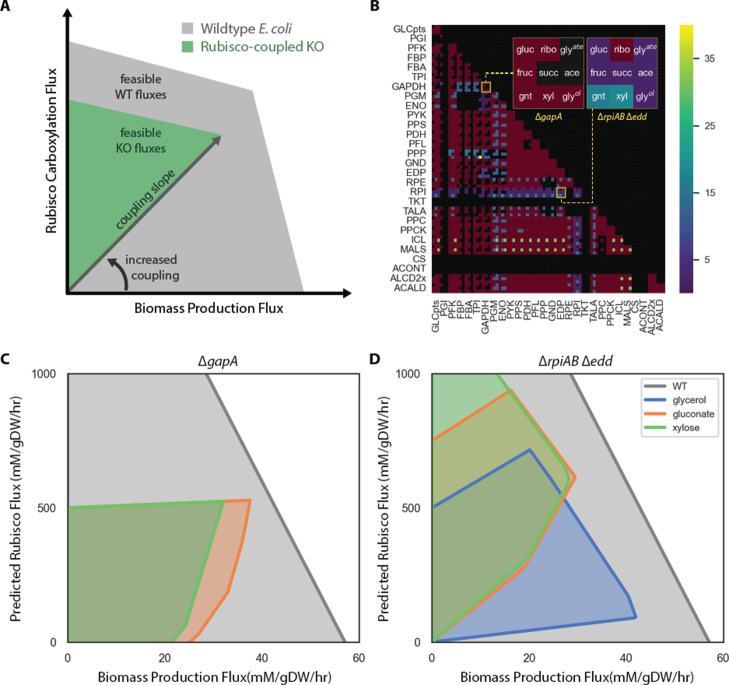
(A) Ribose-5-phosphate (Ri5P) is required for nucleotide biosynthesis. Deletion of ribose-phosphate isomerase (Δrpi) in CCMB1 blocks ribulose-5-phosphate (Ru5P) metabolism in the pentose phosphate (PP) pathway. Expression of rubisco (H. neapolitanus CbbLS) and phosphoribulokinase (S. elongatus PCC7942 prk) on the p1A plasmid (B) permits Ru5P metabolism, thus enabling growth on M9 glycerol media in 10% CO2 (C). Mutating the rubisco active site (p1A CbbL-) abrogates growth, as does mutating ATP-binding residues of Prk (p1A Prk-). (D) CCMB1:p1A grows well under 10% CO2, but fails to grow in ambient air. Cells were grown on M9 glycerol media throughout. The algorithmic design of CCMB1 is described in Figure 2—figure supplement 4 and Appendix 1. The mechanism of rubisco-dependence is diagrammed in Figure 2—figure supplement 3. Figure supplement 2 demonstrates growth of CCMB1:p1A on various media, Figure 2—figure supplement 5 demonstrates complementation by a variety of bacterial rubiscos and Figure 2—figure supplement 1 demonstrates anaerobic growth of CCMB1:p1A, establishing that oxygenation is not required for growth. Acronyms: ribulose 1, 5-bisphosphate (RuBP), 3-phosphoglycerate (3PG).