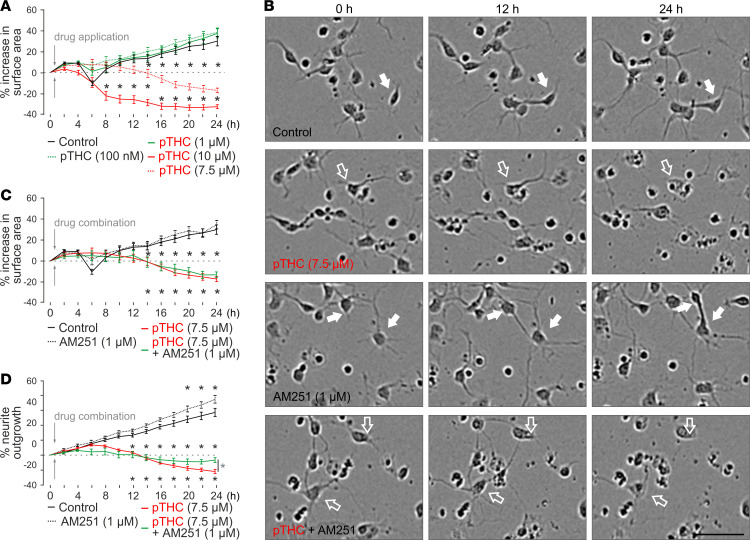
Figure 3. High-throughput time-lapse analysis of THC-induced growth retardation of cortical neurons in vitro.
(A) Plant-derived THC (pTHC) dose-dependently reduced the surface area occupied by neuronal somata, with 10 μM THC inducing significant cell death. (B) Representative phase-contrast images of cultured cortical neurons exposed to the drugs indicated. Solid and open arrows point to live and fragmented neurons, respectively. A THC concentration of 7.5 μM was used that showed a slow and protracted effect, amenable to pharmacological modulation. Scale bar: 50 μm. (C) At 7.5 μM THC concentration, AM251 was ineffective to rescue neuronal survival, as inferred from cell surface area. (D) However, AM251 induced significant recovery of neurite outgrowth at 24 hours (Supplemental Figure 6). Data were collected and analyzed by using an IncuCyte Zoom imaging platform with a loop time of 2 hours. *P < 0.05 (versus control [black] or THC + AM251 [in D, green]; 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc correction). Data were expressed as mean ± SEM with n = 8–18 technical replicates each.