Figure 2.
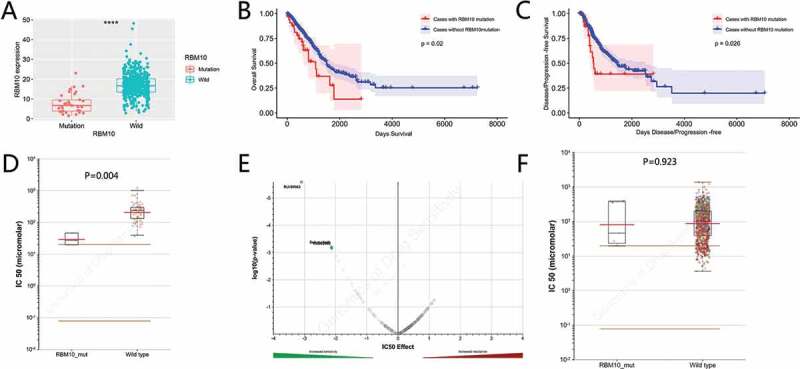
Mutations of RBM10 are associated with lung adenocarcinoma prognosis and drug selection. (a) Correlation between the RBM10 mutation and mRNA expression. (b,c) Kaplan–Meier survival and disease recurrence curves for lung adenocarcinoma patients stratified by the RBM10 mutation. (d,e) Reproduction of the GDSC database by excluding cancer of other types showed that lung adenocarcinoma cells with the RBM10 mutation was also significantly inhibited by RU-SKI43(p = 0.0044200). (f) Scattered plot and volcano plot show that multiple cancer cell types with the RBM10 mutation were not inhibited by RU-SKI43 (p > 0.05)
