Figure 1.
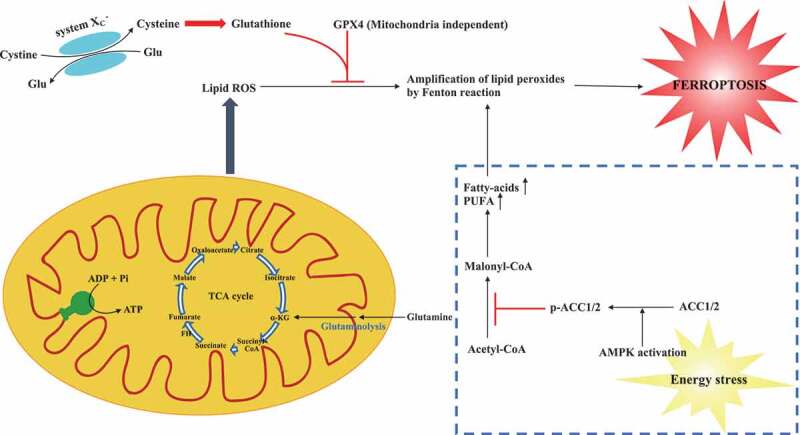
A schematic model describes the roles of energy metabolism in ferroptosis. Inhibiting system XC – (cysteine glutamate transporter) or GPX4 can trigger ferroptosis induced by the accumulation of lipid ROS. Mitochondria metabolism including TCA cycle promotes cysteine deprivation-induced ferroptosis and energy–stress-mediated AMPK activation inhibits ferroptosis. TCA cycle: tricarboxylic acid cycle; α-KG: α-ketoglutarate; ROS: reactive oxygen species; Glu: glutamate; GPX4: glutathione peroxidase 4; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; AAC1/2: acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 and 2; PUFA: polyunsaturated fatty acid
