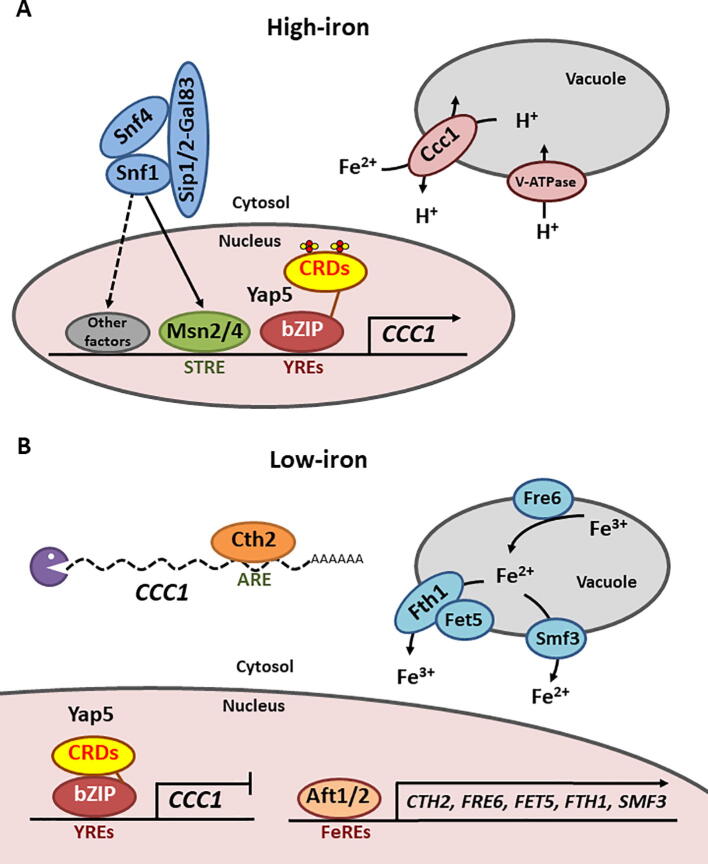
Fig. 4.
Regulation of S. cerevisiae CCC1 in response to iron overload and depletion. A) High-iron conditions. During iron overload, two ISCs associate to the CRDs of DNA-bound Yap5 leading to a conformational change that promotes CCC1 transcription. CCC1 expression is also activated by the Snf1 effectors Msn2/Msn4 and other unknown transcriptional factors. Ccc1 facilitates the import of Fe2+ into the vacuole while exporting H+. Therefore, pH and V-ATPase function are tightly connected to cellular iron homeostasis. B) Low-iron conditions. During iron depletion, Aft1/Aft2 activate the iron regulon, including FRE6, FET5, FTH1 and SMF3 genes, which encode for the vacuolar iron export machinery, and CTH2, which promotes the degradation of CCC1 mRNA. The decrease in ISC synthesis prevents the activation of Yap5, which is constitutively bound to YREs within CCC1 promoter. ARE: AU-rich element; bZIP: basic leucine-zipper domain; CRD: cysteine-rich domain; FeRE: iron regulatory element; STRE: stress response element; V-ATPase: vacuolar ATPase; YRE: Yap5 response element.