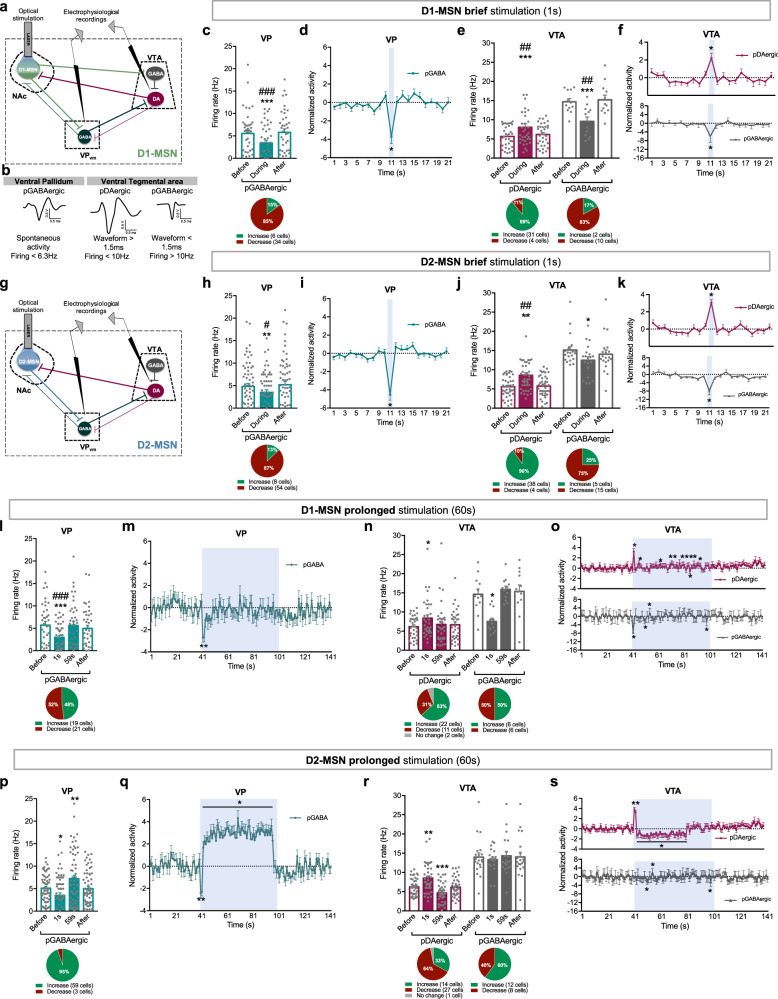
Fig. 4.
Distinct electrophysiological responses of VP and VTA during brief or prolonged MSNs stimulation. a NAc D1-MSN circuitry. b Representative waveform of a VP pGABAergic neuron, and VTA pGABAergic and pDAergic neurons. Pie charts represent the percentage of each type of response to stimulus; bar graphs represent net firing rate before, during and after optogenetic stimulation; blue stripe in scatterplots represents optogenetic stimulus. c Brief D1-MSNs optical stimulation decreases the net firing rate of VP pGABAergic neurons. d Temporal variation of VP activity; note the decrease in activity during optical stimulation (blue). e The same stimulation increases the net activity of VTA pDAergic neurons; conversely, pGABAergic neurons decrease activity. f Temporal variation of VTA neurons activity. g NAc D2-MSNs circuitry. Brief D2-MSNs optical stimulation induces a similar response in VP and VTA regions as D1-MSNs brief stimulation (h–k). l Prolonged D1-MSNs optical stimulation decreases the average VP firing rate in the first second of stimulation; then net activity normalizes to baseline during the rest of the stimulation. m Temporal variation of VP activity. n Prolonged D1-MSNs stimulation induced an increase in the average firing rate of VTA pDAergic neurons in the first second of stimulation, contrary to pGABAergic neurons, that decreased activity. o Temporal variation of the activity of VTA neurons. Note the opposing patterns of activity in pDAergic and pGABAergic neurons. p Prolonged optical stimulation of D2-MSNs decreases the activity of VP neurons in the first second of stimulation, and increases it during the rest of the stimulation. q Temporal variation of VP activity; note the decrease in activity during the first seconds of optical stimulation, and the increase thereafter. r This same stimulation increased the average firing rate of VTA pDAergic neurons in the first second of stimulation, and decreased their activity after. No changes were found in the activity of VTA pGABAergic neurons. s Temporal variation of the activity of VTA neurons. “*” Before vs. during; “#” during vs. after; *p < 0.05, ** or ##p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Data are represented as mean ± SEM