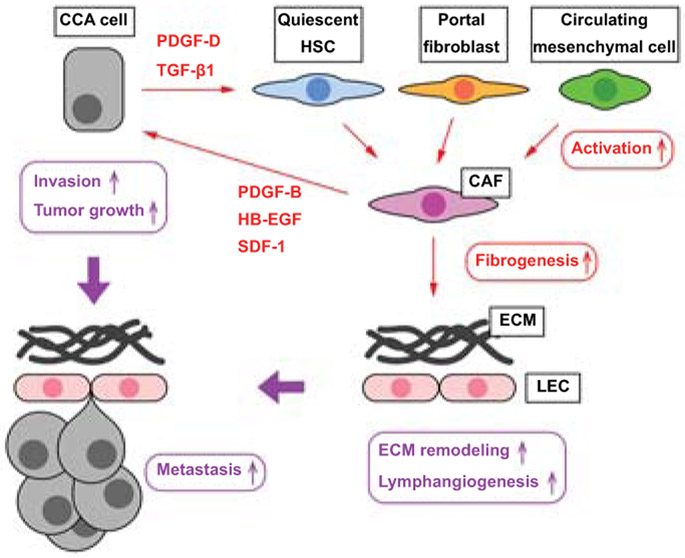
Figure 2. The crosstalk between CCA cells and CAFs.
CCA cells secrete mediators such as PDGF-D and TGF-β1, which induce differentiation of hepatic stellate cells, portal fibroblasts, or circulating mesenchymal cells into activated CAFs. CAFs secrete mediators including PDGF-B, HB-EGF, and SDF-1 leading to CCA tumor growth and invasion. CAFs also contribute to fibrogenesis, leading to ECM remodeling, and to lymphangiogenesis, promoting CCA invasion through the lymphatic endothelial cell (LEC) barrier. This tumor microenvironment is proficient to CCA progression and metastases.