Fig. 1.
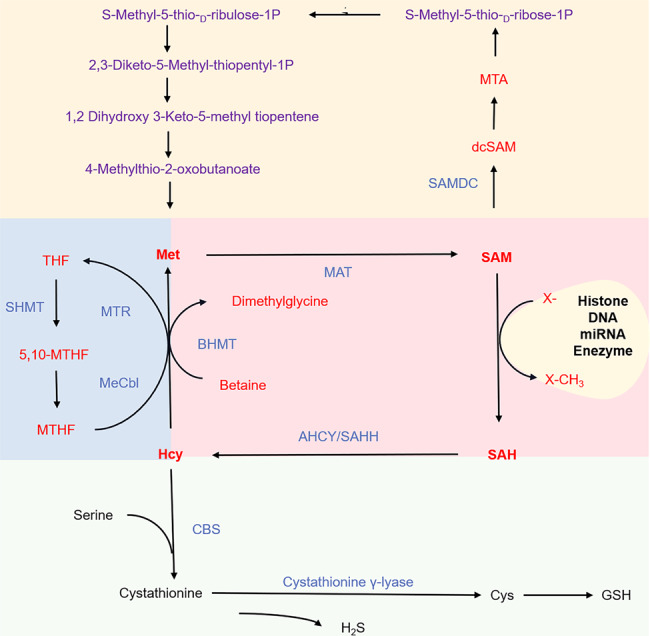
Response of methionine metabolism in the liver. There are four main participants in this pathway, namely methionine, S-adenosylmethionine (SAM), S-adenosyl homocysteine (SAH), and homocysteine (Hcy). Methionine adenosyltransferase (MAT) converts methionine to SAM and then uses a methyl donor catalyzed methyl donor. Another product of these reactions is SAH, which is reduced by S-adenosine homocysteine protease (AHCY/SAHH) to adenosine and Hcy. Methionine metabolism involves the folate cycle, the transsulfuration pathway, and the salvage pathway. AHCY adenosylhomocysteinase, BHMT betaine homocysteine methyltransferase; GSH glutathione; Hcy homocysteine, SAM S-adenosylmethionine, SAH S-adenosyl homocysteine, Met methionine, MTs methyltransferase, CBS cystathionine-β-synthase, Cbl cobalamin, vitamin B12, MeCbl methylcobalamin, MTA 5′‐methylthioadenosine, dcSAM decarboxylated SAM, MTHFR methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase, SHMT serine hydroxymethyltransferase
