Fig. 3.
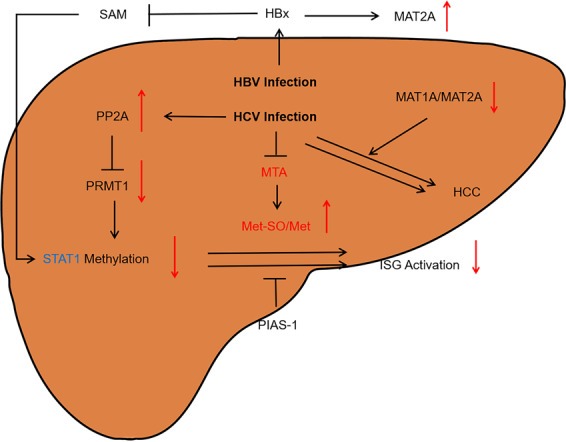
The metabolism of methionine in viral infections of hepatitis B and C. The hepatic polyamine synthesis and transsulfuration pathway activities are impaired in virus infection. Methylthioadenosine (MTA) is a sulfur-containing adenine nucleoside produced from SAM during the synthesis of polyamines, including spermine and spermidine. The level of MTA significantly decreases during the late stage of HCV infection in cells. Moreover, Met is particularly susceptible to elevated ROS levels. Upon reacting to ROS, protein-bound Met is readily oxidized to form methionine sulfoxide (Met-SO). The increased Met-SO level and Met-SO/Met ratio indicate increased oxidative stress subsequent to decrease liver function. Furthermore, the STAT-1 genes showed significant difference between HBV and HCV. Met methionine, Met-SO methionine sulfoxide, HBx the X protein of HBV, ISG interferon-stimulated gene, PP2A protein phosphatase 2A, PRMT1 protein arginine methyltransferase 1, PIAS protein inhibitor of activated STATs
