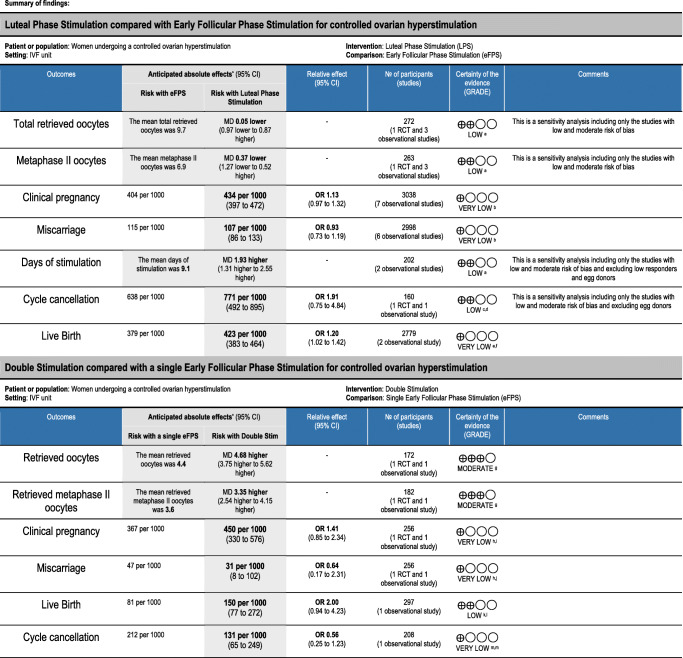
Table 4.
Summary of findings table
*The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI)
CI, confidence interval; MD, mean difference; OR, odds ratio
GRADE Working Group grades of evidence
High certainty: We are very confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect
Moderate certainty: We are moderately confident in the effect estimate: The true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different
Low certainty: Our confidence in the effect estimate is limited: The true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect
Very low certainty: We have very little confidence in the effect estimate: The true effect is likely to be substantially different from the estimate of effect
aOne RCT and 2 retrospective cohorts with low/moderate risk of bias. Main reason for downgrading is the study design
bMost studies are cohorts and before-after, and four with serious/critical risk of bias. Main reasons for downgrading are limitations due to study design and confounding
cOne RCT and one retrospective cohorts with moderate risk of bias. Main reason for downgrading is the study design
dConfidence interval is wide, showing that LPS could reduce slightly the cancelation rate or increase it a lot
eTwo cohort studies with critical risk of bias (the larger with 90% of the weight is retrospective). Main reasons for downgrading are limitations due to study design and unbalanced confounding
fConfidence interval is wide, showing that LPS could increase or have no effect on liver birth rate
gOne RCT with unclear risk for randomization method and allocation concealment and one before-after cohort with critical risk of bias. Main reason for downgrading is the study design
hOne RCT with unclear risk for randomization method and allocation concealment and one retrospective cohort with moderate risk of bias. Main reason for downgrading is the study design
iConfidence interval is wide, showing that Double stimulation could reduce or increase the clinical pregnancy rate
jConfidence interval is wide, showing that Double stimulation could reduce or increase the miscarriage rate
kOne small prospective cohort with moderate risk of bias. Main reason for downgrading is the study design
lConfidence interval is wide, showing that Double stimulation could make little or no increase in live birth rate, or it could be a large increase in live birth rate
mOne small retrospective cohort with critical risk of bias. Main reason for downgrading is the study design and limitations in confounding
nConfidence interval is wide, showing that Double stimulation could reduce or increase the cancelation rate