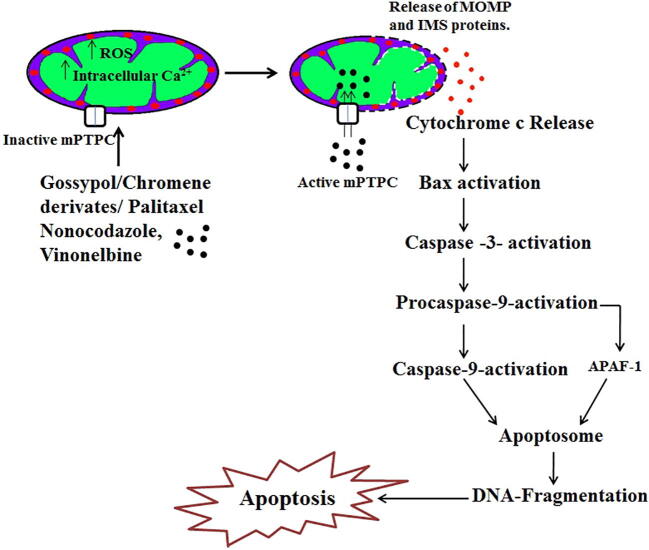
Fig. 3.
Schematic representation of mitochondria-specific targeted drug action. Drug (Paclitaxel/Gossypol/Chromene derivate/Nocodazole/Vinonelbine) induces the increase of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and intracellular calcium level in mitochondria that changes mitochondria permeability transition (MPT) and mitochondria permeability transition pore complex (mPTPC) resulting in solute influx and release of mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP) and mitochondrial intermembrane space (IMS) proteins present in the mitochondrial membrane. The release of cytochrome c activates Bax that in turn activates caspase-3. This induces procaspase-9 followed by activation of apoptotic protease activating factor 1 (APAF-1) which form the apoptosome that leads to DNA fragmentation resulting in apoptosis. Most of the mitochondrial specific anticancer drugs results in induction of apoptosis.