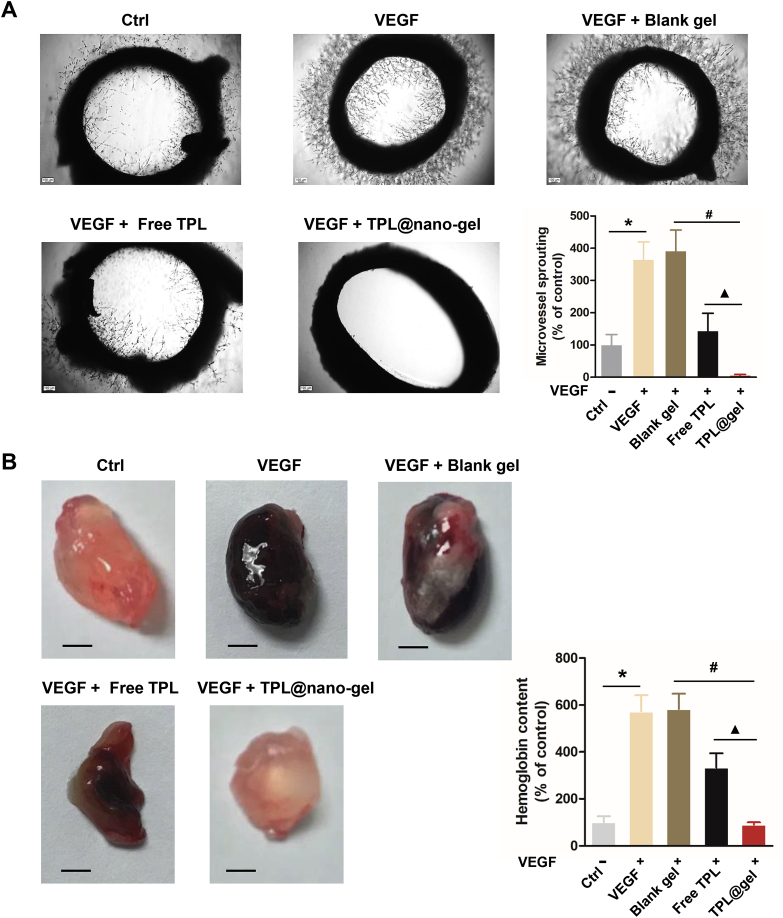
Figure 8.
TPL@nano-gel inhibited angiogenic activity of aorta ring sprouting ex vivo and VEGF-induced angiogenesis matrigel plug in vivo. (A) Representative photographs of micro-vessel sprouting in rat aortic rings. Rat aortic rings were embedded in matrigel and treated with TPL formulations with 20 nmol/L of TPL in the presence of VEGF (100 ng/mL) for 10 days. Then the micro-vessel growth was recorded by an inverted microscope and the number of micro-vessel sprouting was quantified by ImageJ software. Aortic rings VEGF (100 ng/mL) served as positive control. Scale bar = 100 μm. Quantitative analysis of micro-vessel sprouting in each group. (B) Representative photographs of blood vessels formation in matrigel plugs. 6-Week-old BALB/c male mice were subcutaneously injected with 0.5 mL of growth factor-reduced matrigel containing VEGF (250 ng) and heparin (100 Unit) with TPL formulations with 20 nmol/L of TPL. After 14 days, the animals were sacrificed and the matrigel plugs were removed, photographed and weighted. Scale bar: 2.5 mm. To quantify the formation of functional blood vessels, the amount of hemoglobin was measured using the Drabkin reagent Kit (mean ± SD, n = 3), ∗P < 0.05, VEGF alone group vs. the control group, #P < 0.05, TPL@nano-gel vs. blank gel, and ▲P < 0.05, TPL@gel vs. free TPL group.