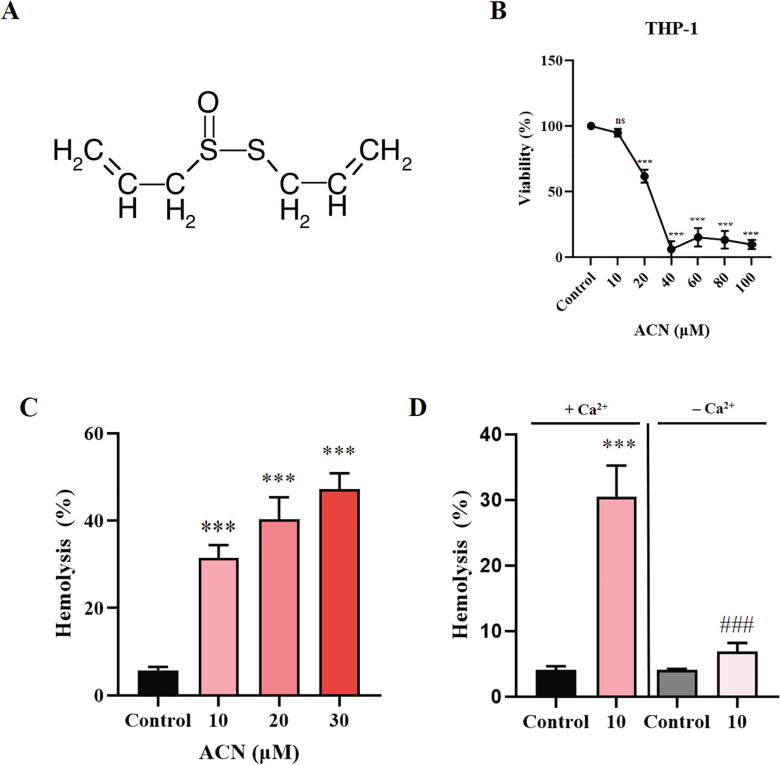
Fig. 1.
Cytotoxicity of ACN to THP-1 cells and RBCs. (A) ACN molecular structure. (B) Cells were treated with the vehicle control or with 10–100 µM ACN for 24 h at 37 °C and cytotoxicity was assessed based on the MTT assay. (C) Arithmetic means ± SEM (n = 9) of ACN-induced dose-dependent hemolysis. Cells were treated with the vehicle control or with ACN at 10–30 µM for 24 h at 37 °C and hemolysis was assessed based on hemoglobin release in the medium. (D) Effect of extracellular calcium removal on ACN-induced hemolysis. Cells were treated with the vehicle control or with 10 µM ACN, in HBSS or Ca2+-free HBSS, for 24 h at 37 °C, and hemolysis was subsequently measured. ns (P > 0.05) indicates insignificant difference from control. ***(P < 0.001) indicates significant difference from control. ###(P < 0.001) indicates significant difference from the corresponding condition in presence of calcium (ANOVA).