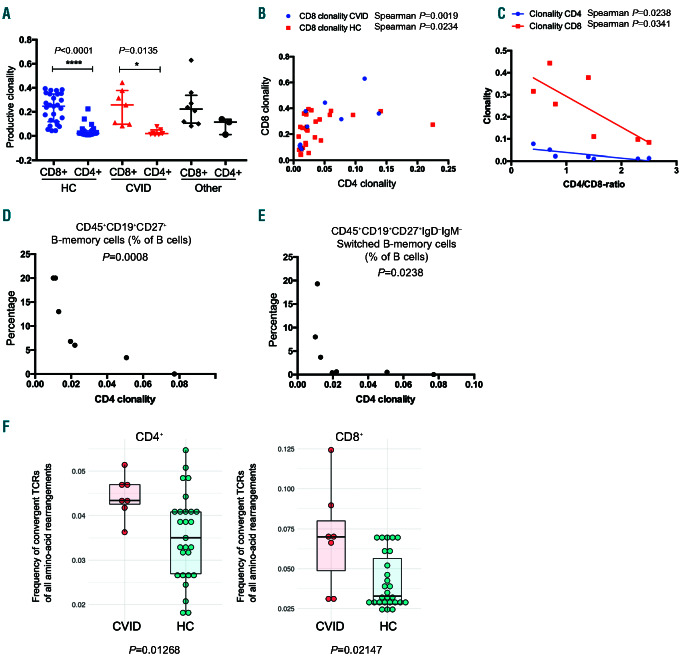
Figure 3.
T-cell repertoire characteristics in common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) patients. (A) Clonality indices of CD4- and CD8-cell productive T-cell receptor (TCR) rearrangements. No statistically significant differences were seen between patients and healthy controls, but CD8+ cells were more clonal than CD4+ cells. Other: immunodeficiency patients other than CVID. Statistical testing comprised a Kruskall-Wallis test as an omnibus test and Dunn multiple comparison tests as post-hoc tests. Medians and interquartile ranges are shown. (B) CD4+ and CD8+ clonality indices correlate with each other, but not in a linear fashion. (C) Low CD4/CD8 ratios are associated with higher CD8 clonality. (D) Increased CD4+ clonality is associated with decreased frequency of memory B cells in CVID patients (Spearman correlation, P=0.0008). (E) Increased CD4+ clonality is associated with decreased frequency of switched memory B cells in CVID patients (P=0.0238). (F) CVID patients show a higher frequency of convergent TCR of all TCR amino-acid rearrangements (Mann-Whitney test, P=0.013 for CD4+ and P=0.021for CD8+ ). Vertical lines: median; box hinges: interquartile ranges; whiskers: reasonable extremes of the data; ns: not significant; HC: healthy control; CVID: common variable immunodeficiency; Other: immunodeficiency other than CVID. ****P<0.0001; *P<0.05.