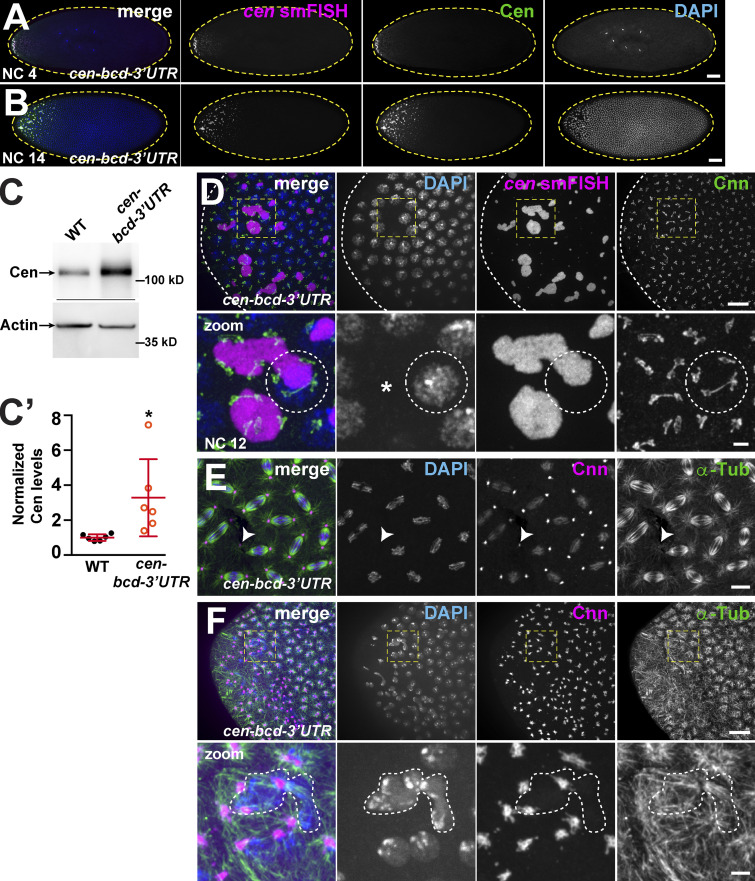
Figure 8.
Ectopic localization of cen mRNA disrupts nuclear divisions. Maximum-intensity projections of cen-bcd-3′UTR embryos (derived from females expressing a pUASp-cen-bcd-3′UTR transgene and the maternal α-Tub GAL4 driver in the cen null background). (A and B) Embryos labeled with cen smFISH (magenta), DAPI (blue), and Cen (green) with a gradient of cen mRNA and protein (A) and disrupted nuclear spacing at the anterior pole (B). (C) Blots show Cen protein in 1–3-h (∼NC 7–NC 14) embryos and quantified in C′. Cen levels were normalized to the mean WT levels of actin from n = 3 independent biological replicates with n = 2 technical replicates run on the same gel. Mean ± SD is displayed (red). *, P < 0.05 by unpaired t test. (D) NC 12 anterior with large cen RNPs (magenta) decorated by centrosomes (Cnn, green). Dashed circle outlines nucleus and part of a cen RNP with supernumerary centrosomes. (E) NC 12 embryo at ∼50% egg length; arrowhead marks a detached centrosome. (F) NC 12 embryo at anterior pole with disorganized microtubules (α-Tub, green), centrosome position (Cnn, magenta), and dysmorphic nuclei (DAPI; dashed lines). Boxes enlarged below (zoom). Scale bars: 50 µm (A and B); 10 µm (D–F); and 2 µm (insets).