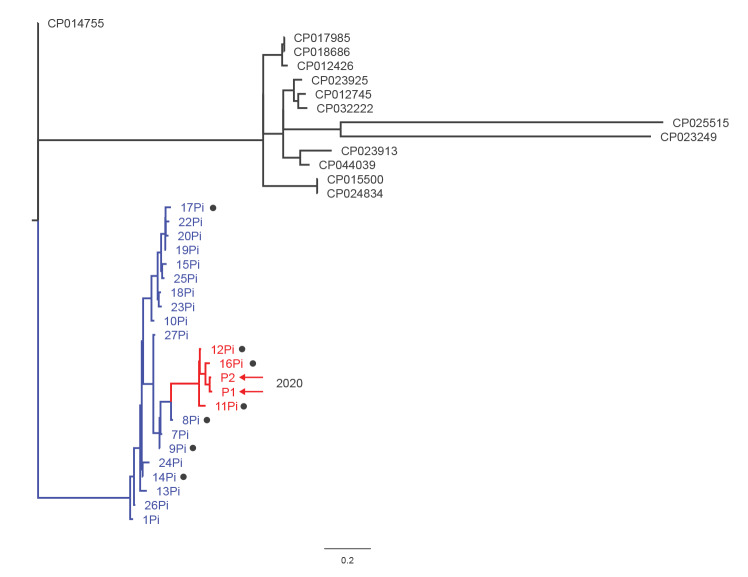
Figure.
Phylogenetic tree to analyse ST147 Klebsiella pneumoniae sequences from isolates of two patients in Pisa, Italy, 2020 (n = 36 sequences)
CDS: coding sequence; SNP: single nucleotide polymorphism; ST: sequence type.
All sequences analysed in the phylogenetic analysis are of ST147. The parsimony SNP analysis was performed by the kSNP3 (Galaxy version 3.1) software at the ARIES public Galaxy server (https://w3.iss.it/site/aries/). The phylogenetic tree was visualised using the Fig Tree programme v. 1.4.3 (http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/). The phylogenetic tree was based on the sequences of Kp-P1 and Kp-P2 genomes (highlighted by red arrows) as well as those of 34 genomes, including 21 from strains isolated during the 2018–2019 outbreak in Pisa (in blue or red font) and 13 from epidemiologically-unrelated strains (in black). The sequences of the 13 unrelated strains were downloaded from GenBank (accession numbers are indicated on the tree leaves). Black dots indicate the seven genomes selected for protein alignment analysis (https://rast.nmpdr.org/seedviewer.cgi). Translations of the CDSs in these genomes were aligned to those of Kp-P1 and Kp-P2 genome CDSs for comparison. The scale bar indicates the extent of genetic change by estimating the average number of nucleotide substitutions per site.