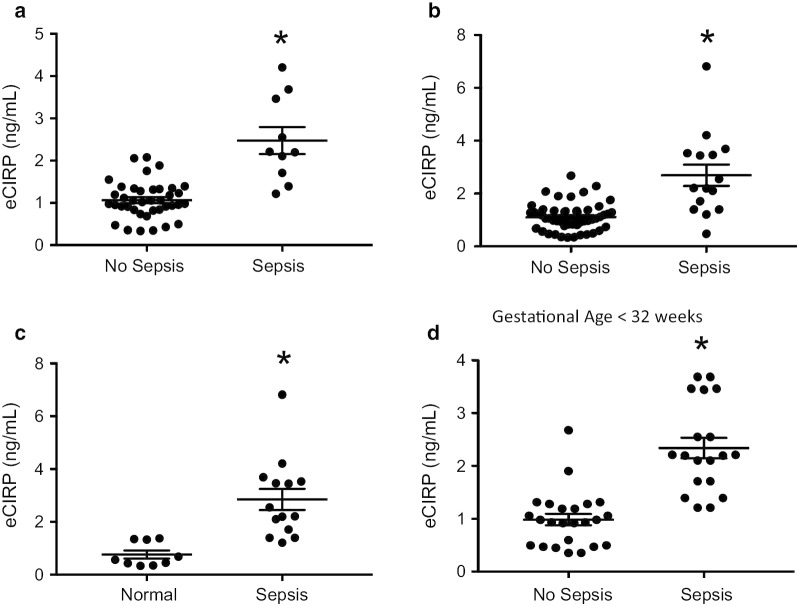
Fig. 1.
Serum eCIRP levels are elevated in septic neonates. Serum levels of eCIRP were compared in a neonates classified as non-septic (N = 39) versus septic (N = 10) according to the electronic medical record. b Infants clinically classified as “sepsis rule-out” were divided into the non-septic (N = 52) vs septic (N = 15) cohorts according to duration of antibiotics therapy. c Serum levels of eCIRP in full term, well infants (N = 9) were compared to septic neonates (N = 14). d Infants with a gestational age < 32 weeks of no sepsis (N = 24) vs sepsis (N = 19) were compared. Data are expressed as means ± SE and compared by two-tailed student’s t test (* p < 0.05 vs no sepsis)