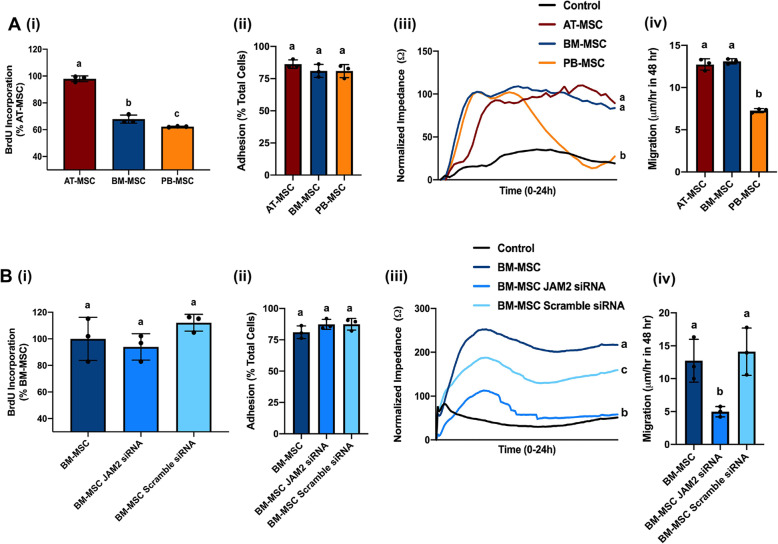
Fig. 3.
Knock down of junctional adhesion molecule 2 (JAM2) in bone marrow (BM)-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) alters cell motility. a Base line measurements in MSCs derived from donor-matched adipose tissue (AT), bone marrow (BM), and peripheral blood (PB) of cell proliferation rate, as determined by incorporation of 5-Bromo-2′-deoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation (i); cell adhesion as measured by centrifugation assay (ii); cell invasion through an equine endothelial cell (EC) monolayer, as determined by electric cell impendence sensing (ECIS) (iii); and cell migration, as determined by an in vitro scratch assay (iv). b Measurements in BM-derived MSCs that were either not transfected or transfected with JAM2-specific siRNA or scramble siRNA (control) of cell proliferation rate, as determined by incorporation of 5-Bromo-2′-deoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation (i); cell adhesion as measured by centrifugation assay (ii); cell invasion through an equine endothelial cell (EC) monolayer, as determined by electric cell impendence sensing (ECIS) (iii); and cell migration, as determined by an in vitro scratch assay (iv). Significant differences are depicted by different letters, n = 3. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. P < 0.05