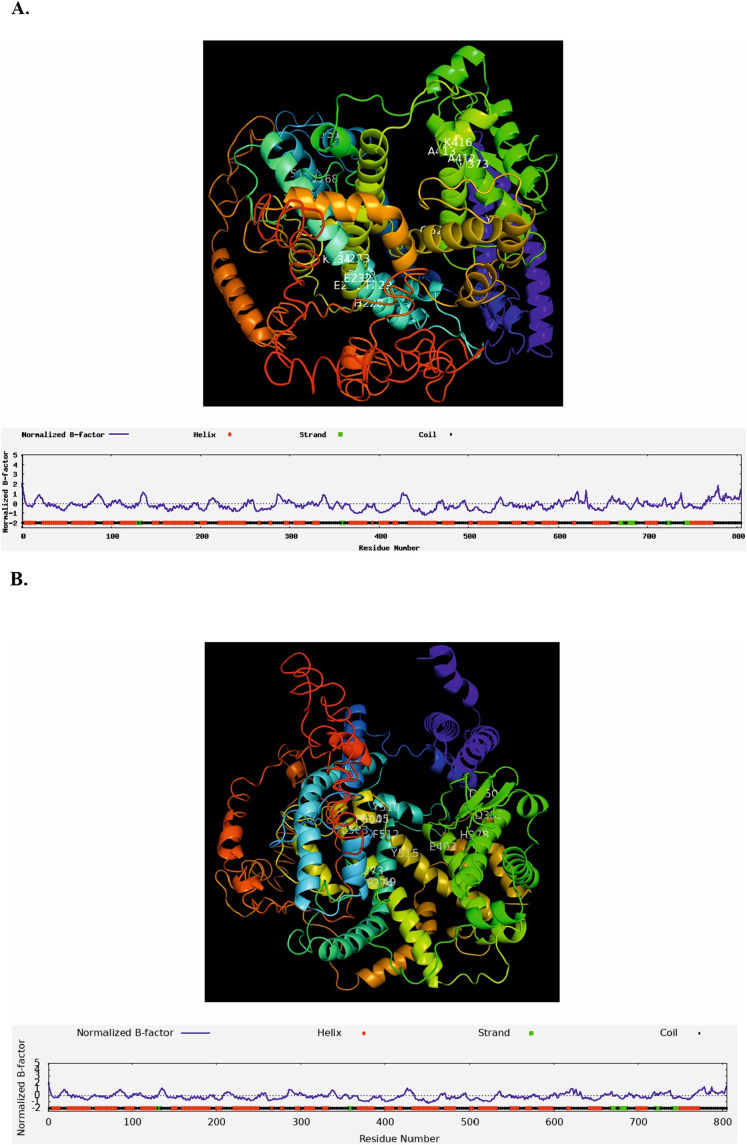
Fig. 7.
3D structure prediction and ligand binding sites prediction of native ACE2 and ACE2 with rs149039346 and rs147311723. (A) 3D structure of native ACE2 and possible ligand binding site residues predicted as 151, 167, 168, 169, 228, 229, 230, 231, 232, 233, 234, 373, 381, 412, 413, 416, 522; (B) 3D structure of ACE2 with rs149039346 (S692P) and possible ligand binding site residues predicted as 273, 274, 350, 378, 382, 402, 449, 503, 504, 505, 510, 512, and 515; (C) 3D structure of ACE2 with rs147311723 (L731F) and possible ligand binding site residues predicted as 151, 167, 168, 169, 228, 229, 230, 231, 232, 233, 234, 373, 381, 412, 413, 416, 522; (D) enzyme commission (EC) numbers and active sites (402, and 515) are shown for native ACE2 and with rs149039346 and rs147311723. B-factor is a value indicating the extent of the inherent thermal mobility of residues/atoms in proteins. Based on the distributions and predictions of the B-factor profile (BFP), residues with BFP values higher than 0 are less stable in experimental structures.