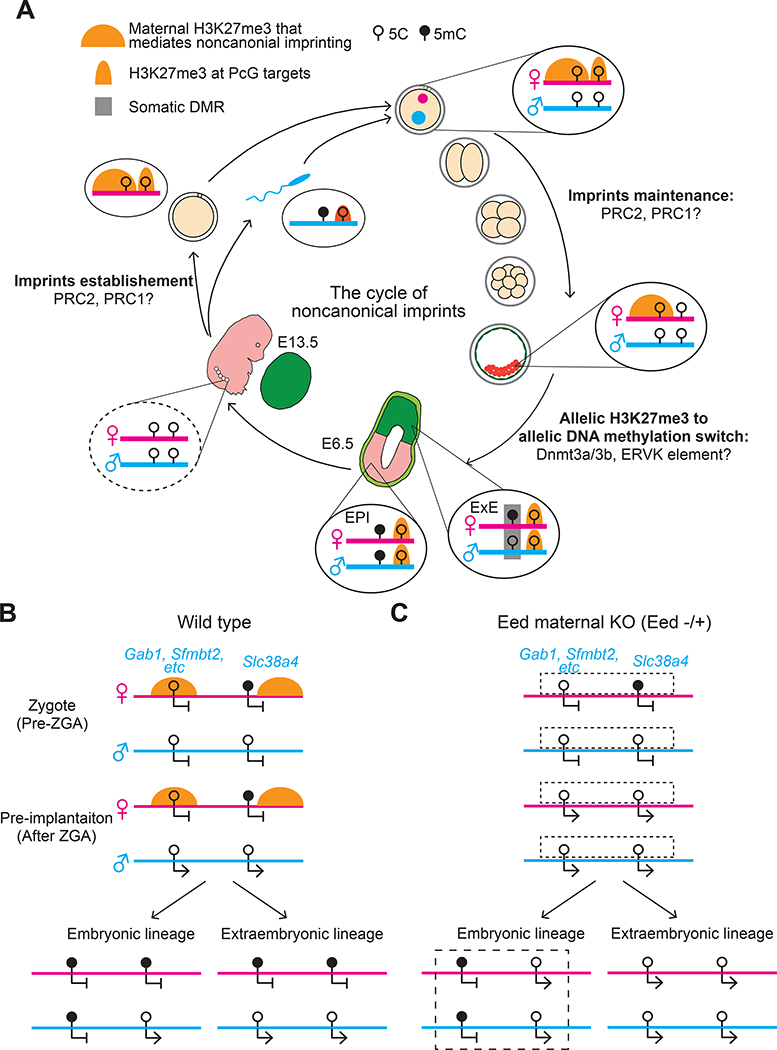
Figure 2. Oocyte inherited H3K27me3 initiates noncanonical imprinting.
A) The figure depicts the dynamics of H3K27me3 at noncanonical imprinting loci and at genomic targets of Polycomb group (PcG) proteins. Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) mediates H3K27me3 deposition during oogenesis; whether PRC1-mediated H2AK119ub is involved in PRC2 function in oogenesis remains unknown. After fertilization, H3K27me3 at PcG targets is largely reprogrammed, but maternally inherited H3K27me3 at noncanonically imprinted loci is maintained during pre-implantation development and is responsible for silencing the maternal allele of these genes. After implantation, H3K27me3 is re-established at PcG targets whereas the maternal H3K27me3 that initiates noncanonical imprinting disappears from both the epiblast (EPI) and extraembryonic ectoderm (EXE). The maintenance of some noncanonical imprinting in EXE depends on the acquisition of somatic differentially methylated regions (DMRs) during implantation via the DNA methyltransferases DNMT3A and DNMT3B. Active endogenous virus-K (ERVK) long terminal repeats (LTR) in the somatic DMRs may have a role in the maintenance of noncanonical imprinting in the placental lineage. In the epiblast, both alleles at noncanonically imprinted loci are repressed by DNA methylation. In primordial germ cells (PGCs), DNA methylation at noncanonical imprinting loci is expected to be erased (dashed line) during the wave of global DNA demethylation mediated by TET1 and DNA replication.
B) The typical dynamics of H3K27me3 and DNA methylation at noncanonically imprinted loci (represented by Gab1) in wild type mice (Ba) and Eed maternal knockout (KO) mice (Bb) are shown. Oocyte-specific depletion of EED, an essential subunit of PRC2, causes loss of H3K27me3 in mature oocytes. Embryos that develop from Eed-null oocytes (that is, Eed maternal KO embryos) lack maternally-provided H3K27me3 and lose noncanonical imprinting in both pre-implantation embryos and extraembryonic cells. Furthermore, somatic DMRs are unmethylated on both alleles in EXE of these embryos. The Slc38a4 locus differs from other noncanonically imprinted loci because its DMR is established during oogenesis. However, it becomes hypomethylated in Eed maternal KO EXE, suggesting that maternal H3K27me3 is essential to maintain differential DNA methylation at this locus. DNA methylation status of the loci in embryonic lineages of Eed maternal KO has not been analyzed, but predicted patterns are included and indicated by dashed boxes. ZGA: zygotic genome activation.