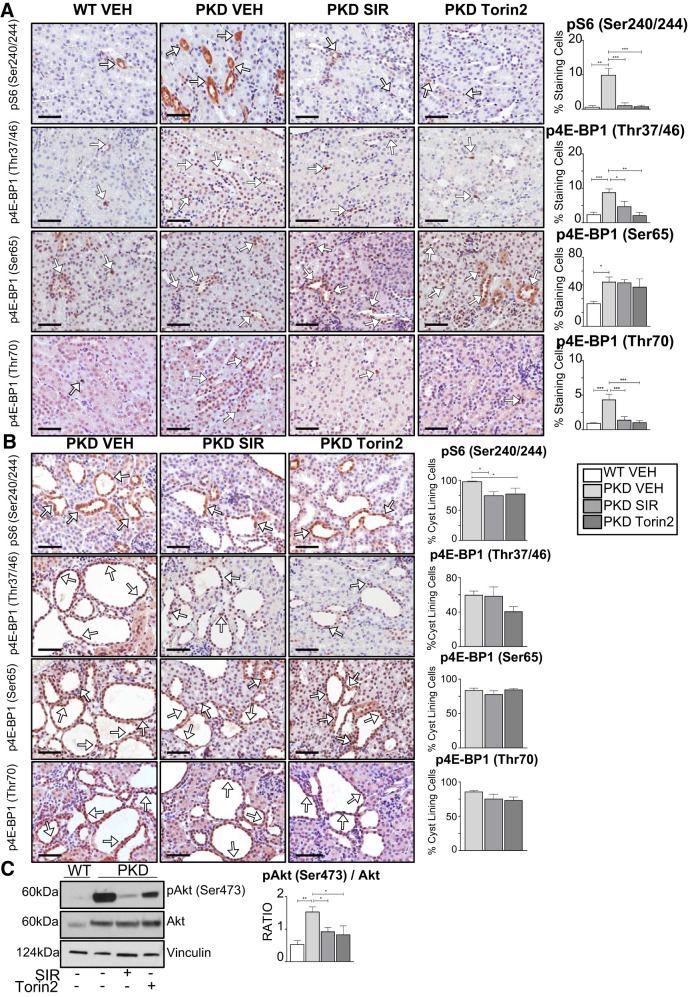
Fig. 4.
Effect of sirolimus (SIR) versus torin2 on mechanistic target of rapamycin complex (mTORC)1 [phosphorylated S6 (pS6) and phosphorylated eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1 (p4E-BP1)] and mTORC2 [phosphorylated Akt (pAkt) (Ser473)] in Pkd1RC/RC kidneys. The effect of sirolimus or torin2 treatment on pS6 and p4E-BP1 (Thr37/46, Ser65, and Thr70) was determined in kidneys from mice with polycystic kidney disease (Pkd1RC/RC) and wild-type (WT) mice by immunohistochemical analysis. A: pS6 (Ser240/244) and p4E-BP1 (Thr37/46, Ser65, and Thr70) staining in noncystic tubules, expressed as the percentage of cells staining positive per 240-µm2 area (%staining cells). White arrows indicate 3,3′-diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride hydrate-positive cells. Scale bars = 50 µm. B: pS6 (Ser240/244) and p4E-BP1 (Thr37/46, Ser65, and Thr70) staining in cyst-lining cells, expressed as the percentage of positive-staining cells per cyst (%cyst-lining cells). White arrows indicate 3,3′-diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride hydrate-positive cells. Scale bars = 50 µm. C: pAkt (Ser473) Akt sensitivity to torin2 and sirolimus in Pkd1RC/RC kidneys. The ratio of pAkt to total Akt was quantitated by densitometry. Values are means ± SE; n = 4–5 per group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 (by ANOVA with a Newman-Keuls post test).