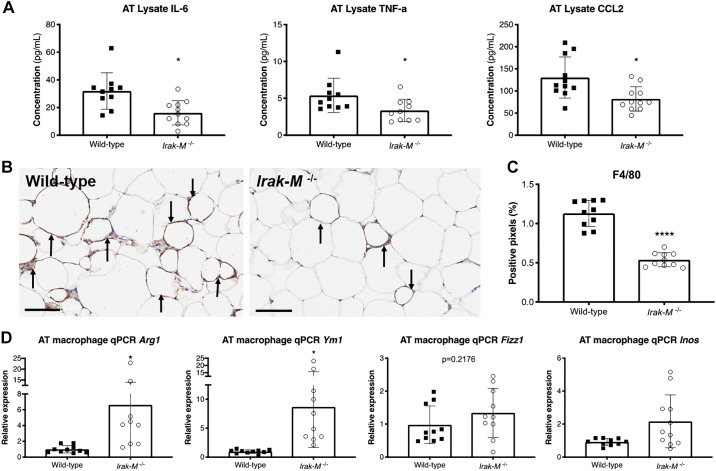
Fig. 9.
Deficiency in Irak-M reduces adipose tissue inflammation, macrophage infiltration, and skews macrophages toward an alternatively activated M2-like phenotype after 12 wk of HFD. A: ELISA of adipose tissue lysate of wild-type (WT) and Irak-M−/− mice (n = 10–11 per group) for interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor α (TNF), and c-c motif chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2). B: immunohistochemical staining of F4/80 in adipose tissue of WT (left) and Irak-M−/− mice (right). Arrows indicate the crown-like structures (CLS) formed by macrophage aggregation in HFD-fed mice. The black bars indicate 100 μm. C: quantitative analysis of positive pixels for F4/80 stain (n = 10 animals per group, mean of 10 tissue sections per animal). D: qPCR analysis for M1/M2 markers (Arg1, Ym1, Fizz1, and Inos/Nos2) of macrophages isolated from adipose tissue (n = 9–11 per group). *P < 0.05, ****P < 0.0001.