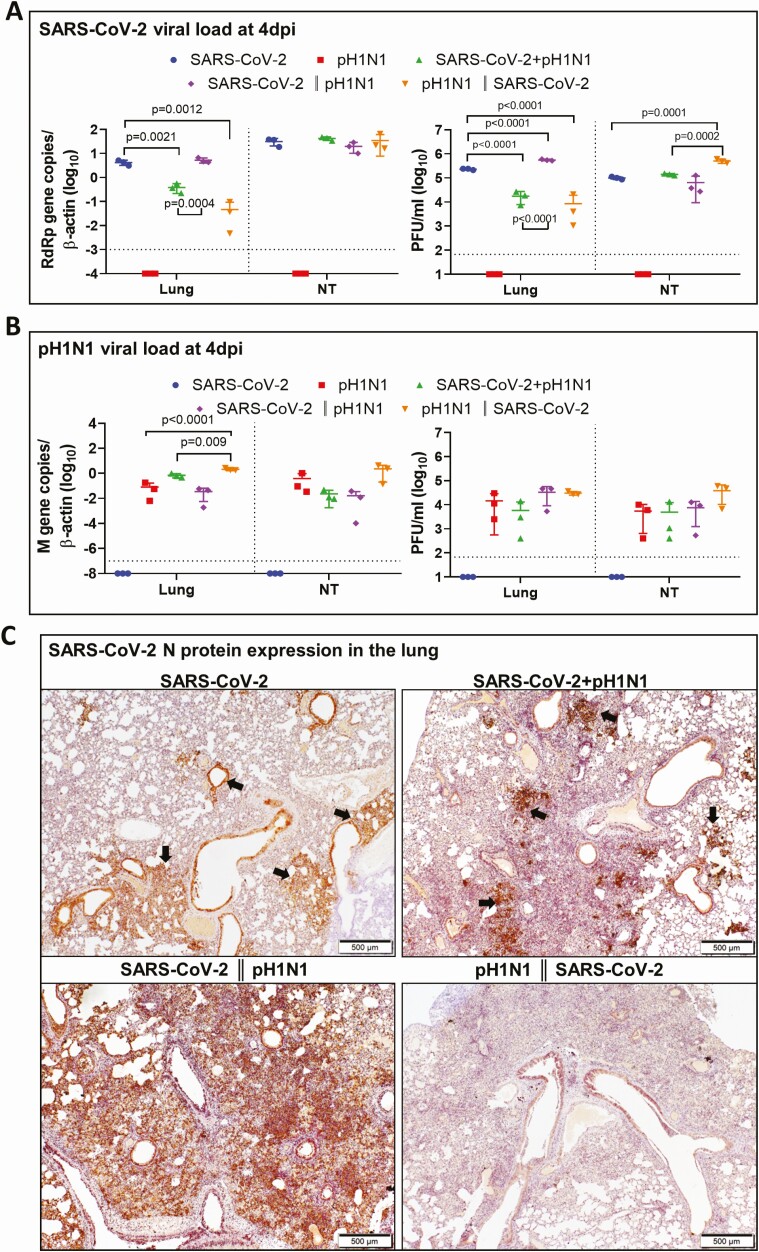
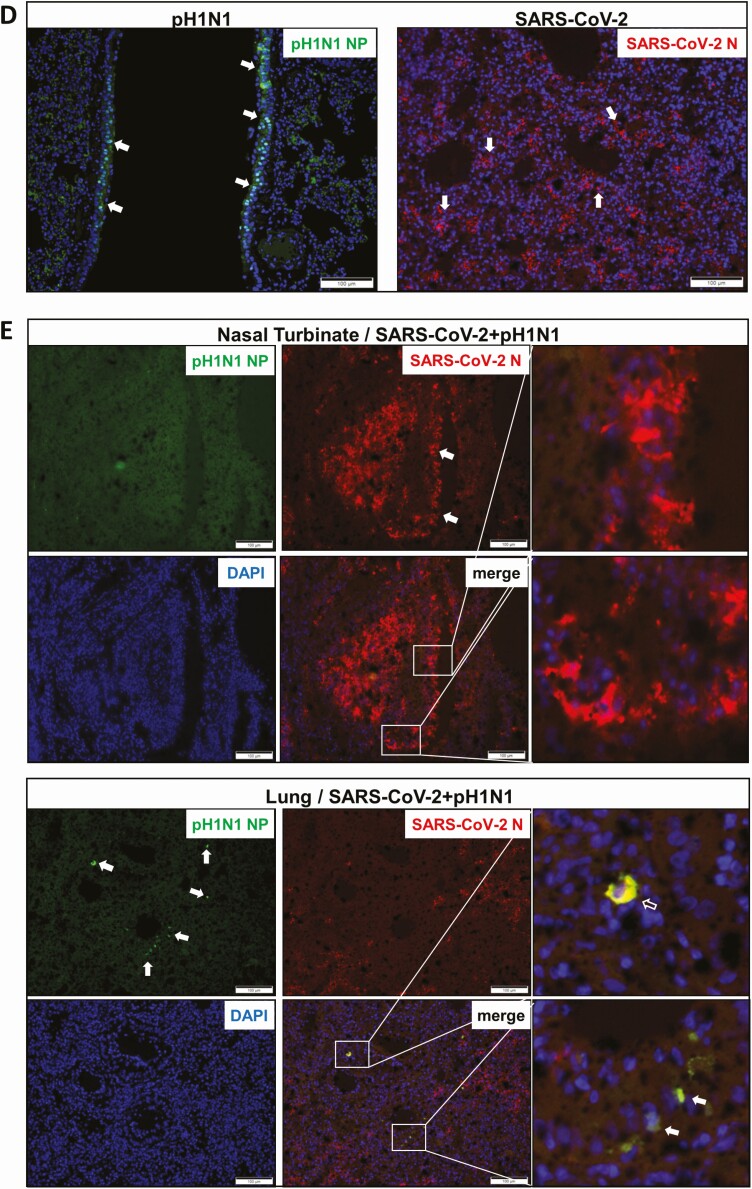
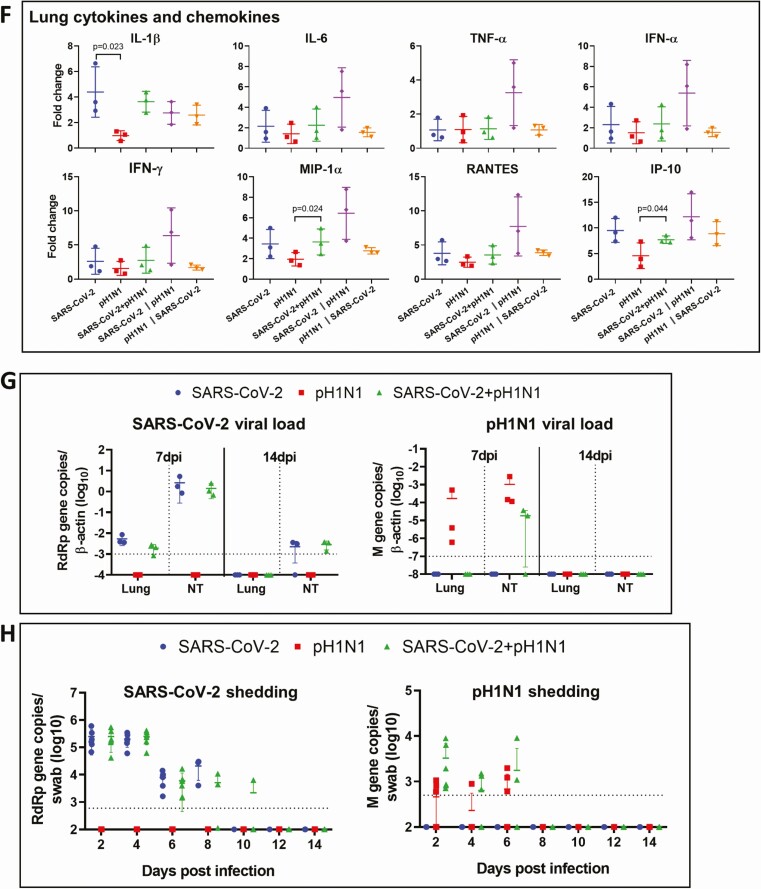
Figure 4.
Viral replication profiles in the lung and nasal turbinate (NT) tissue of hamsters after monoinfection, simultaneous, or sequential coinfection. A, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) viral load in lung and NT tissues. SARS-CoV-2 RdRp gene copies determined by real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) (left panel). SARS-CoV-2 infectious viral titers were determined by plaque assays in Vero E6 cells (right). n = 3 each group. P values are calculated by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Error bars indicate mean ± standard deviation (SD). Horizontal dashed line indicates detection limit of the assays. B, Mouse-adapted A/Hongkong/415742/2009 H1N1 (pH1N1) viral load in lung and NT tissues by RT-qPCR (influenza A matrix gene, left panel) or plaque assays in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells (right). n = 3 each group. P values are calculated by one-way ANOVA. Error bars indicate mean ± SD. Horizontal dashed line indicates detection limit of the assays. C, Representative images of immunohistochemistry-stained SARS-CoV-2 N protein in the lung tissues after monoinfection or coinfection. SARS-CoV-2 N protein Continued was stained in brown. The images of SARS-CoV-2 monoinfection shows N protein expression in regional alveoli and bronchiolar epithelium (arrows); simultaneously coinfected lung has small patches of N protein expression in a large area of inflammatory consolidated lung tissue (arrows); the lung coinfected sequentially by SARS-CoV-2 prior to pH1N1 (SARS-CoV-2 || pH1N1) shows extensive N protein expression distributed diffusely in the lung, whereas in sequential coinfection by pH1N1 prior to SARS-CoV-2 (pH1N1 || SARS-CoV-2), the large area of inflammatory consolidation in lung tissue shows a few N protein–positive cells. D, Immunofluorescence images illustrate pH1N1 NP antigen and SARS-CoV-2 N antigen in single virus–infected hamster lung tissues. pH1N1 nucleoprotein (NP) is only seen in the epithelium of bronchiolar epithelium, not in alveoli (NP, green). SARS-CoV-2 N antigen is seen diffusely distributed in alveoli (N, red). E, Dual immunofluorescence images illustrate the distribution of pH1N1 NP and SARS-CoV-2 N in simultaneously coinfected hamster NT (upper panels) and lung tissues (lower panels). pH1N1 NP antigen was rarely seen in the coinfected NT tissues, whereas SARS-CoV-2 N protein was abundantly detected (arrows, N stained red). In the lung tissue, the 2 viral antigens also distributed differently. These images show pH1N1 NP expression in a few cells in the bronchiolar epithelium, but not in alveoli (arrows, green), while SARS-CoV-2 N is seen in alveoli (red) but not in bronchiole. Co-localization of SARS-CoV-2 N and pH1N1 NP antigen is shown in a macrophage (magnified image, open arrow). F, Relative expression of inflammatory cytokines/chemokines in hamster lung tissues determined by RT-qPCR using gene-specific primers. G, RT-qPCR determined SARS-CoV-2 viral load (left) and pH1N1 viral load (right) in the lung and NT tissues taken at 7 days postinfection (dpi) or 14 dpi after simultaneous coinfection or monoinfection. n = 3 each group. Error bars indicate mean ± SD. Horizontal dashed line indicates detection limit of the assays. H, SARS-CoV-2 (left) and pH1N1 (right) virus shedding from oral swabs determined by RT-qPCR. Oral swab samples were collected every other day during the 14 days after virus challenge. Error bars indicate mean ± SD. Horizontal dashed line indicates detection limit of the assays. Double vertical lines indicate sequential inoculation (24 hours apart); + indicates simultaneous inoculation. Abbreviations: IP-10, interferon-γ induced protein 10; M gene, influenza A matrix gene; MIP-1α, macrophage inflammatory protein 1 alpha; N, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 nucleocapsid protein; NP, influenza A nucleoprotein; NT, nasal turbinate; pH1N1, mouse-adapted A/Hongkong/415742/2009 H1N1; PFU, plaque-forming unit; RANTES, regulated upon activation, normal T-cell expressed protein; RdRp, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha.