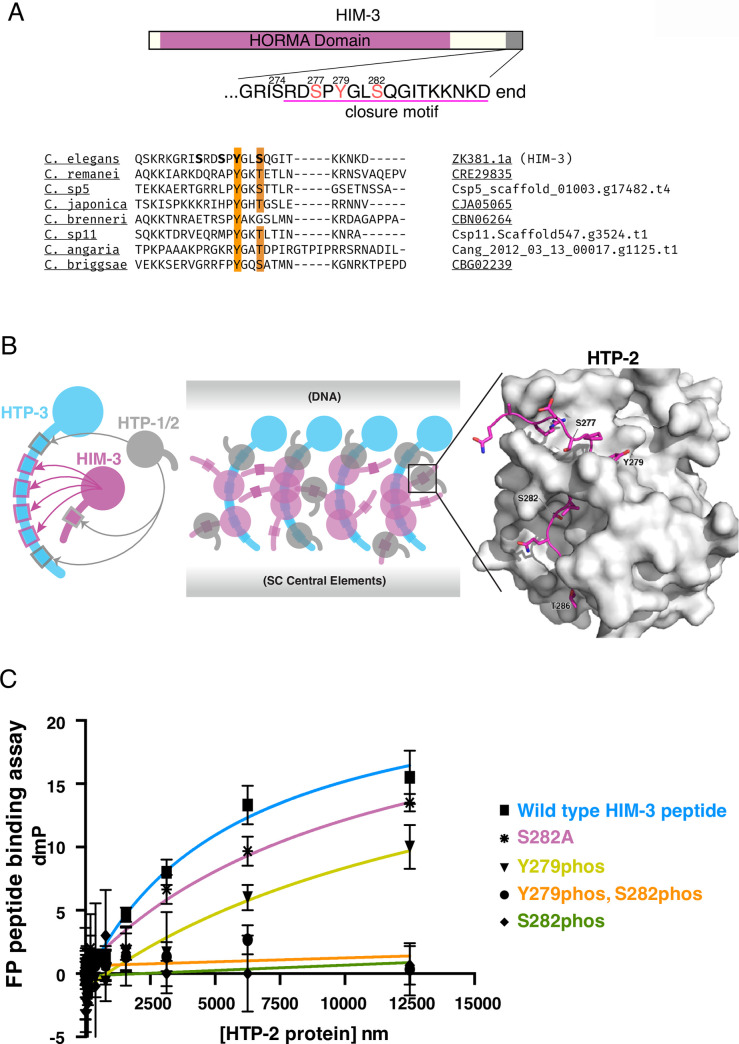
Fig 1. Phosphorylation at the HIM-3 closure motif prevents HTP-1/2 binding in vitro.
A, top: Schematic diagram of HIM-3, showing the HORMA domain (magenta) and phosphorylation sites identified by mass spectrometry in red. The conserved closure motif is underlined. bottom: Conservation of the Tyr and Ser/Thr, highlighted in orange, in the closure motif in eight Caenorhabditis species. B, left: Diagram of hierarchical binding of HTP-1, 2, 3 and HIM-3 from [27]. center, diagram of possible multivalent binding modes of the axial element, based on [36,71]. right, Interactions between the HIM-3 closure motif (magenta) and the HTP-2 (grey) HORMA domain shown in PDB structure 4TZL [27]. C, Fluorescence polarization peptide binding assay using bacterially purified HTP-2 protein (full length) and fluorescently tagged HIM-3 peptides with indicated phosphorylation or Ala substitution. Wild type means HIM-3 peptides with no phosphorylation. Phosphorylation at Ser282 inhibits HTP-2 binding in vitro. Error bars are calculated as the SD from triplicated measurements. Measured Kd values were: 5.8μM for unphosphorylated peptides, not significant binding for S282phos and Y279phos_S282phos peptides, 16.1μM for Y279phos peptides, and 11.3μM for S282A peptides. The binding constants of all the modified HIM-3 peptides are statistically different from unmodified, wild type HIM-3 peptides (two-tailed p value < 0.0001 by unpaired t-test).