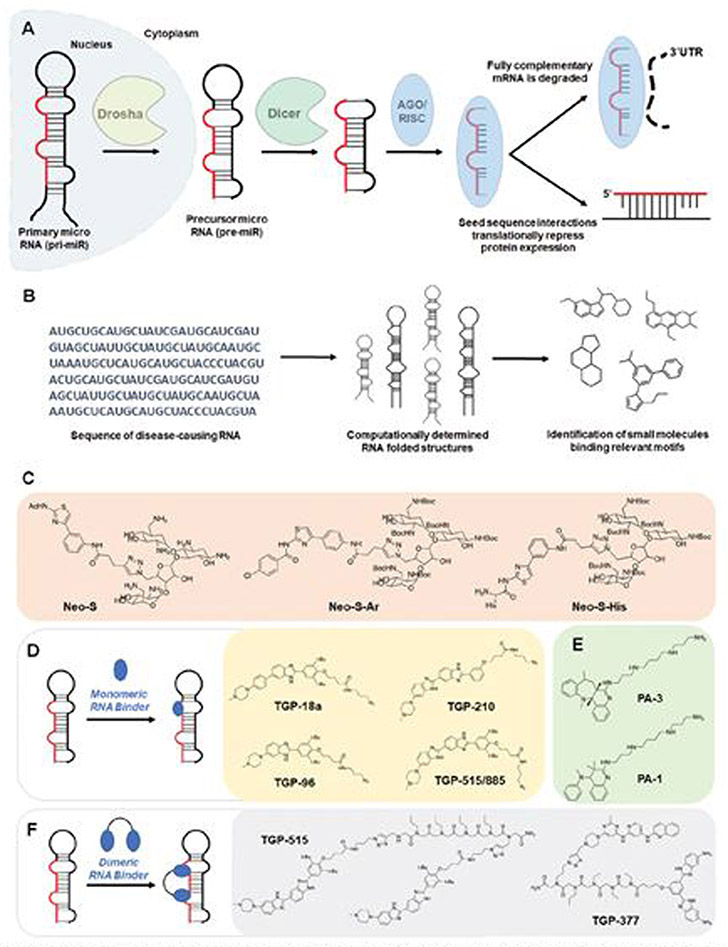
Fig. 2.
Small molecule targeting of miRNAs. (A) Schematic of the biogenesis of miRNAs. Primary miRNAs (pri-miR) are processed by the nuclear RNase III Drosha and exported to the cytoplasm, affording precursor miRNAs (pre-miR), which are then processed by the RNase III endonuclease Dicer. The miRNA duplex is loaded into the AGO/RISC complex, where the duplex is dissociated and acts through either translational repression or mRNA degradation to downregulate target proteins. (B) Workflow schematic of the Inforna hit identification process (C) Structures of neomycin conjugates that inhibit miRNA biogenesis. (D) Schematic of monomeric RNA binder mode of action, blocking functional processing sites on miRNA. Representative chemical structures of these monomers are also shown. (E) Structures of polyamines that inhibit miRNA biogenesis. (f) Dimeric RNA binders have improved potency and selectivity by binding to a functional site and nearby druggable motif simultaneously. Structures of representative miRNA-targeting dimers are shown.