Fig. 1. Identity and the heterogeneity of extracellular vesicles and exosomes.
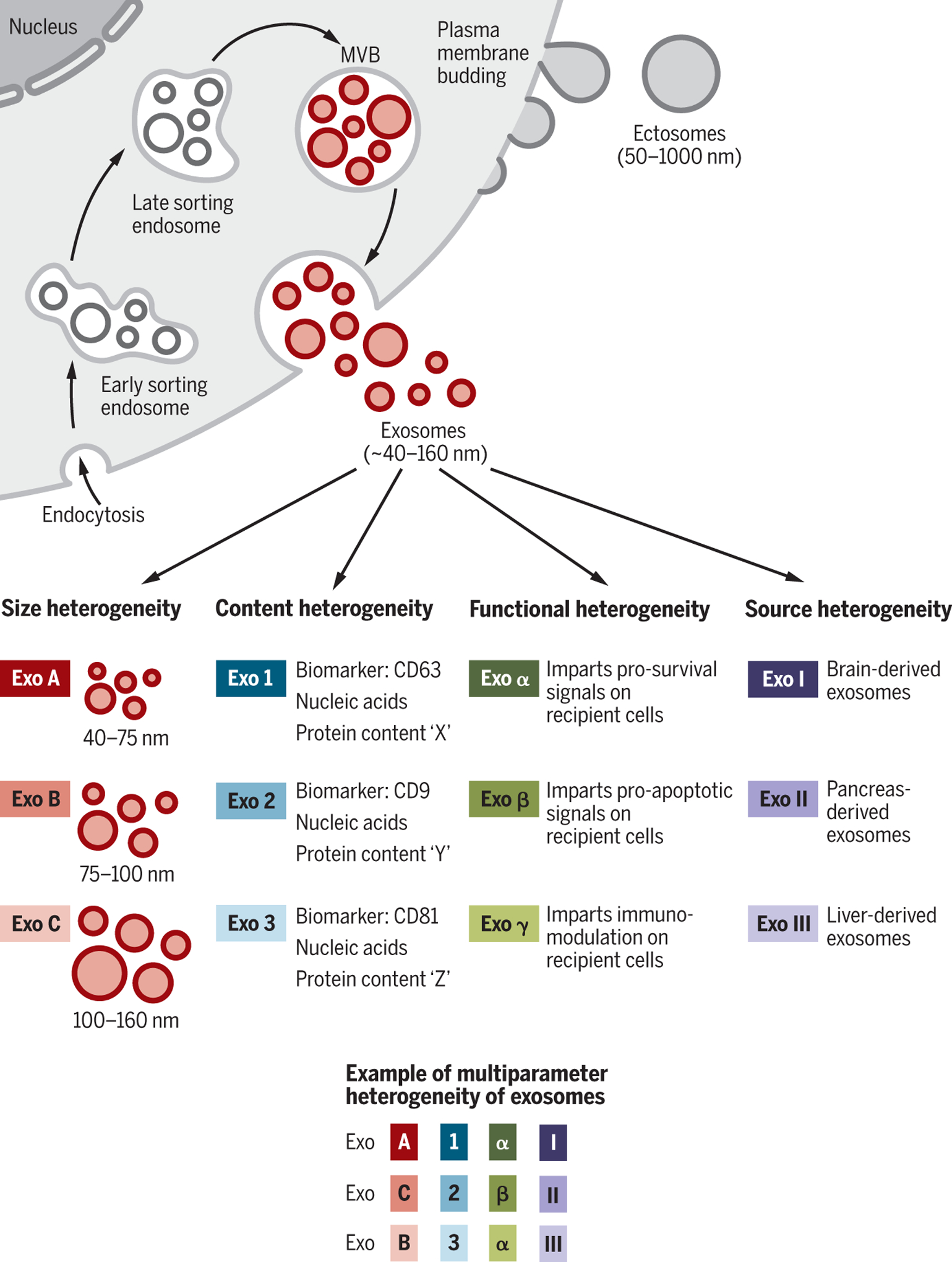
The two major categories of EVs are ectosomes and exosomes. Ectosomes are released through plasma membrane budding and are in the size range of ~50 nm to 1 μm. Exosomes originate from the endosomal pathway by the formation of the ESEs, LSEs, and ultimately MVBs, which contain ILVs. When MVBs fuse with the plasma membrane, exosomes are released (size range ~40 to 160 nm). Exosomes can be a highly heterogeneous population and have distinct abilities to induce a complex biological response. The heterogeneity of exosomes may be conceptualized on the basis of their size, content (cargo), functional impact on recipient cells, and cell of origin (source). Distinct combinations of these characteristics give rise to a complex heterogeneity of exosomes.
