Fig. 3. Cellular journey of internalized exosomes and endogenously produced exosomes.
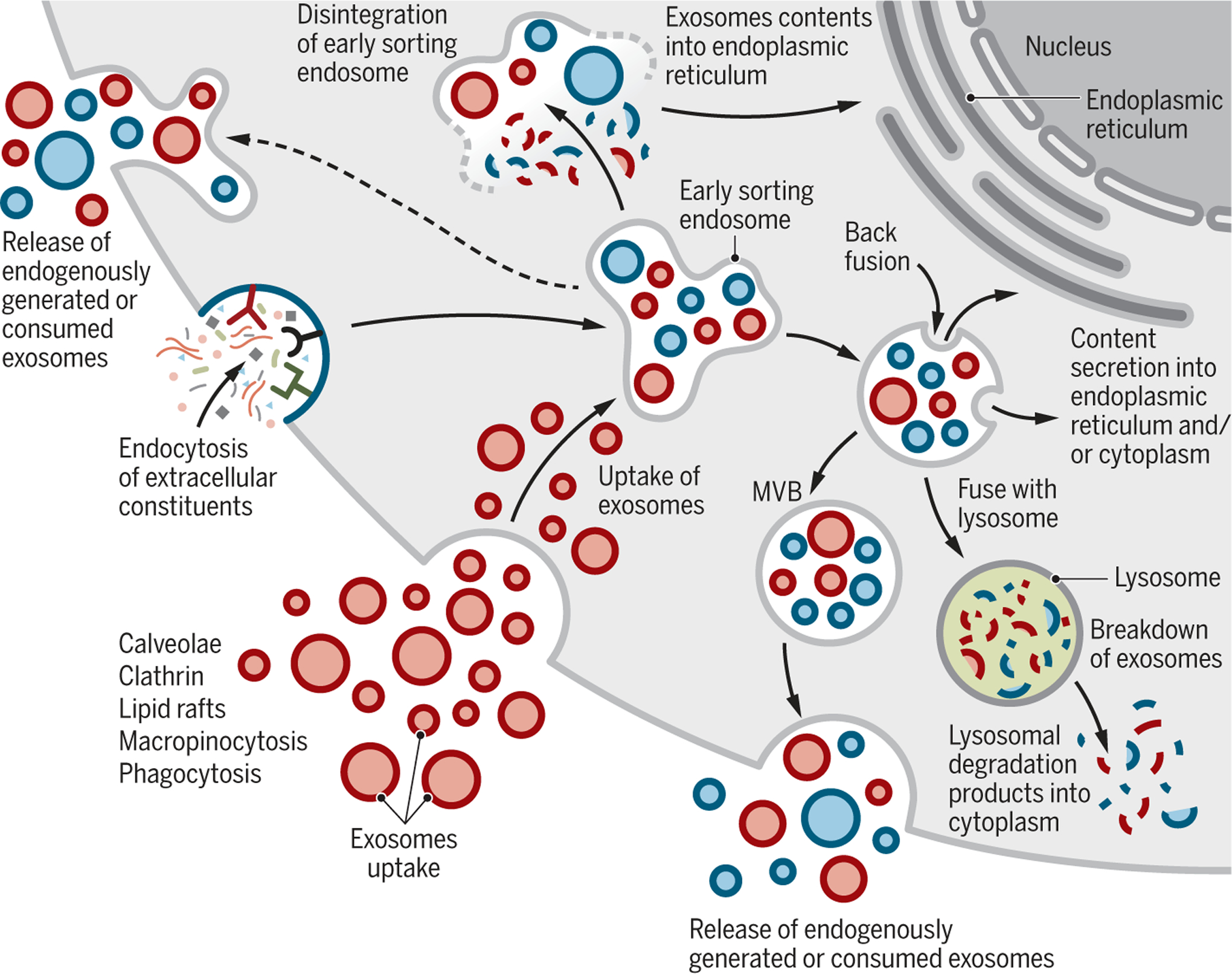
Exosomes may directly enter cells by different mechanisms (red). Exosomes are generated de novo by cells through the endocytosis process (blue). Exosomes are continuously being generated by and taken up by cells. It is likely that they can be secreted as a mixture of the de novo-generated and consumed exosomes (red and blue). It is unknown if the release of endogenously generated or consumed exosomes occurs together or separately. Exosomes that are taken up can get degraded by lysosomes. Exosomes that enter cells may enter or fuse with preexisting ESEs and subsequently disintegrate and release their contents into the cytoplasm. Alternatively, endosomes could fuse back with the plasma membrane and release exosomes outside the cells.
