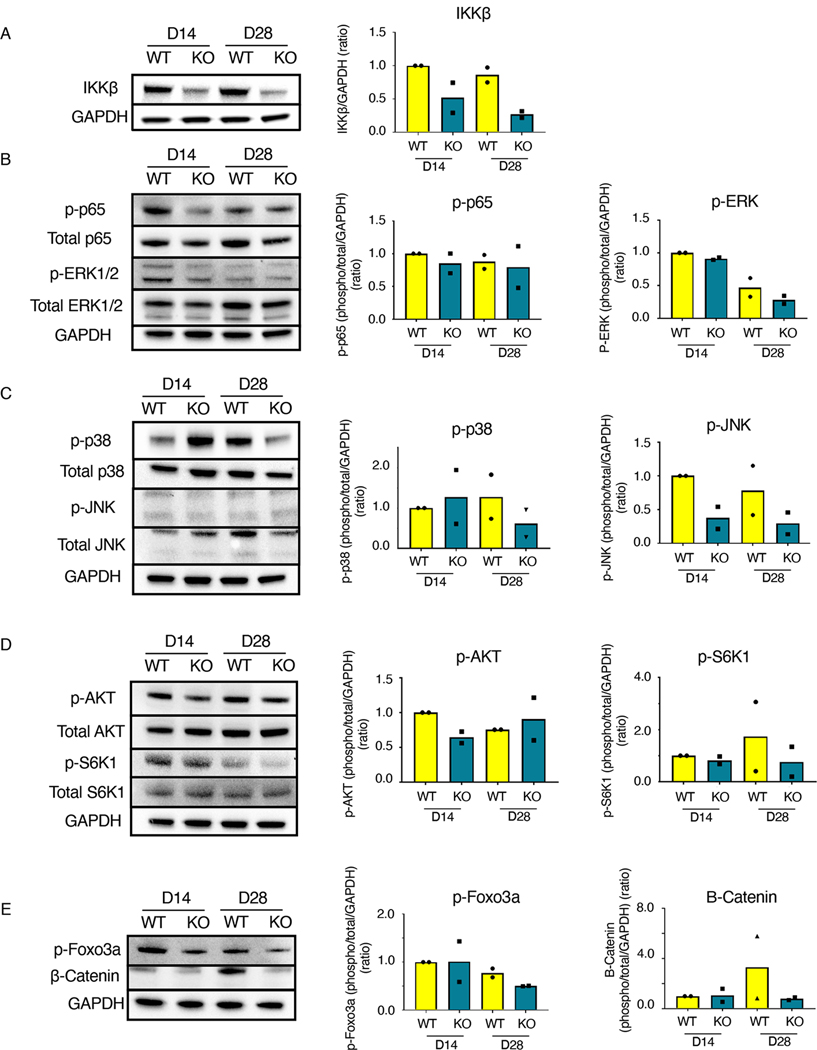
Fig. 4. IKKβKOScx affects several signaling cascades in addition to canonical NF-κB signaling.
Western blots and quantification for the indicated components of NF-κB, MAPK, mTOR, AKT, β-Catenin, and apoptosis signaling in tendons from wild-type and IKKβKOScx mice 14 and 28 days after tendon transection. (A) IKKβ. (B) Total p65, phosphorylated p65 (p-p65), total ERK1/2, and phosphorylated ERK1/2 (p-ERK1/2). (C) Total p38, phosphorylated p38 (p-p38), total JNK, and phosphorylated JNK (p-JNK). (D) Total AKT, phosphorylated AKT (p-AKT), total S6K1, and phosphorylated S6K1 (p-S6K1). (E) β-catenin and phosphorylated Foxo3a (p-Foxo3a). Complete blots for one biological replicate are shown in fig. S4. N=2 independent experiments, with 3 mice pooled per genotype per timepoint for each independent experiment.