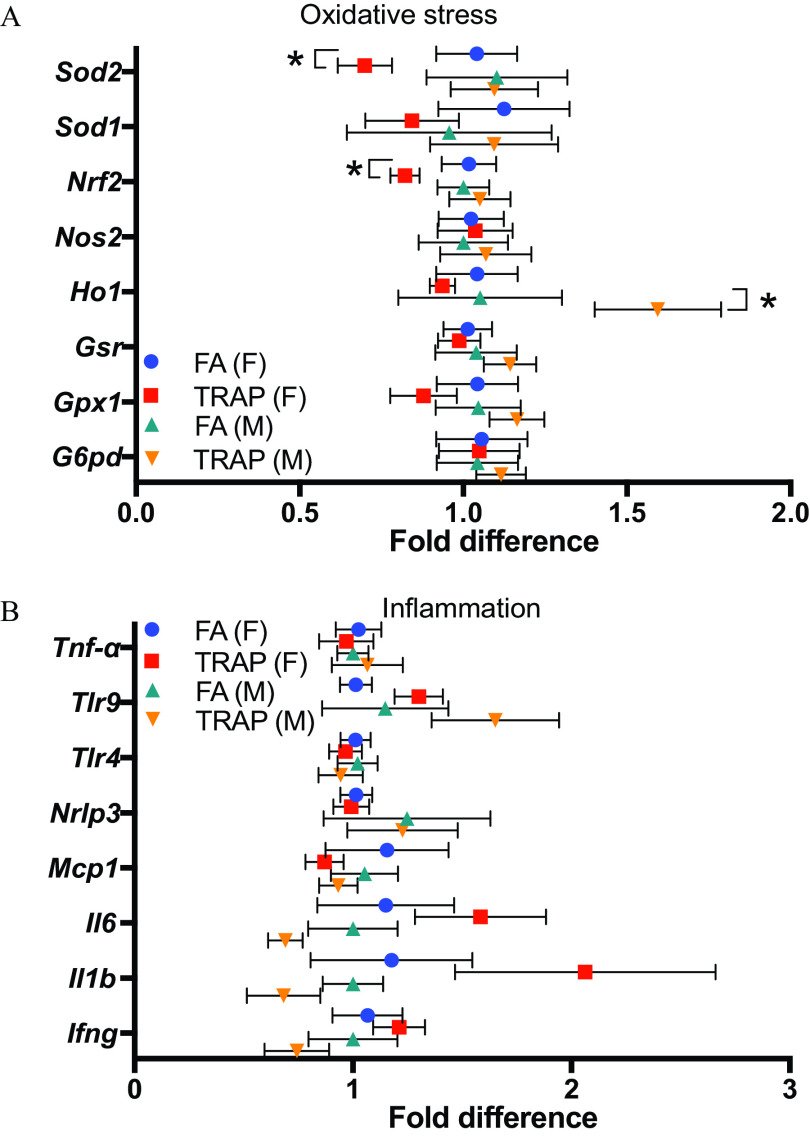
Figure 5.
Expression of oxidative stress and inflammation-related genes were examined in the lung tissues by qRT-PCR. (A) Fold difference of oxidative stress-related genes in lungs from both female and male rats exposed to FA or TRAP. (B) Fold difference of inflammatory genes in lungs from both female and male rats exposed to FA or TRAP. Fold differences in gene expression were calculated by delta delta CT (cycle threshold) method (). All gene expressions were normalized by expression of housekeeping gene beta-actin and FA group was used as a reference group when calculating the values. The formulas are: ; ; Fold gene . Two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Sidak’s multiple comparisons test was used for statistical analysis. ; The exact mean and SEM values for data presented here can be found in Table S7. Note: FA, filtered air; SEM, standard error of the mean; TRAP, traffic-related air pollution. *.