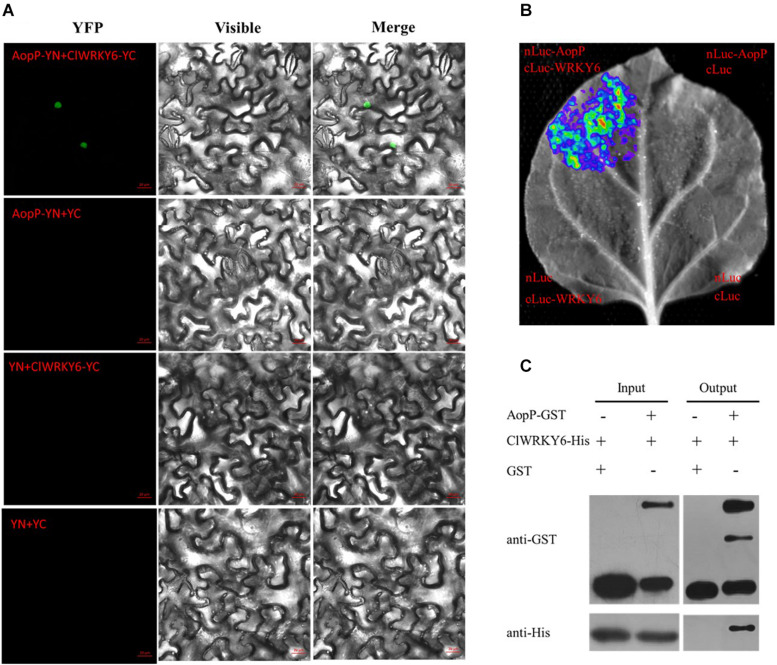
FIGURE 3.
Interaction between AopP and ClWRKY6. (A) AopP interacted with watermelon ClWRKY6 as shown by the BiFC assay. AopP fused with nYFP, and ClWRKY6 fused with cYFP constructs were introduced into GV3101 strains. GV3101 carrying 35S::AopP-nYFP or 35S::ClWRKY6-cYFP were co-injected into Nicotiana benthamiana leaves. After 48 h, leaves were collected and observed using a confocal microscope. The empty vector nYFP or cYFP was used as a negative control. (B) AopP interacted with watermelon ClWRKY6 as observed with the LCI assay. AopP fused with nLUC and ClWRKY6 fused with cLUC constructs were introduced into GV3101 strains. The GV3101 carrying 35S::AopP-nLUC or 35S::ClWRKY6-cLUC were co-injected into N. benthamiana leaves. After 48 h, the leaves were collected and observed using a CCD imaging apparatus (NightSHADE LB985; Berthold). (C) AopP interacted with watermelon ClWRKY6 as indicated by the GST pull-down assay. The AopP was co-purified with ClWRKY6. AopP-GST or GST was incubated with ClWRKY6-His and precipitated by glutathione agarose. The presence of ClWRKY6-His in glutathione agarose-bound protein was detected by anti-His immunoblot. The experiment was independently repeated three times and similar results were obtained.