Figure 5. Effect of six weeks ethanol consumption on p-PSD-95 and t-PDS-95 protein expression in the AcbCo and AcbSh.
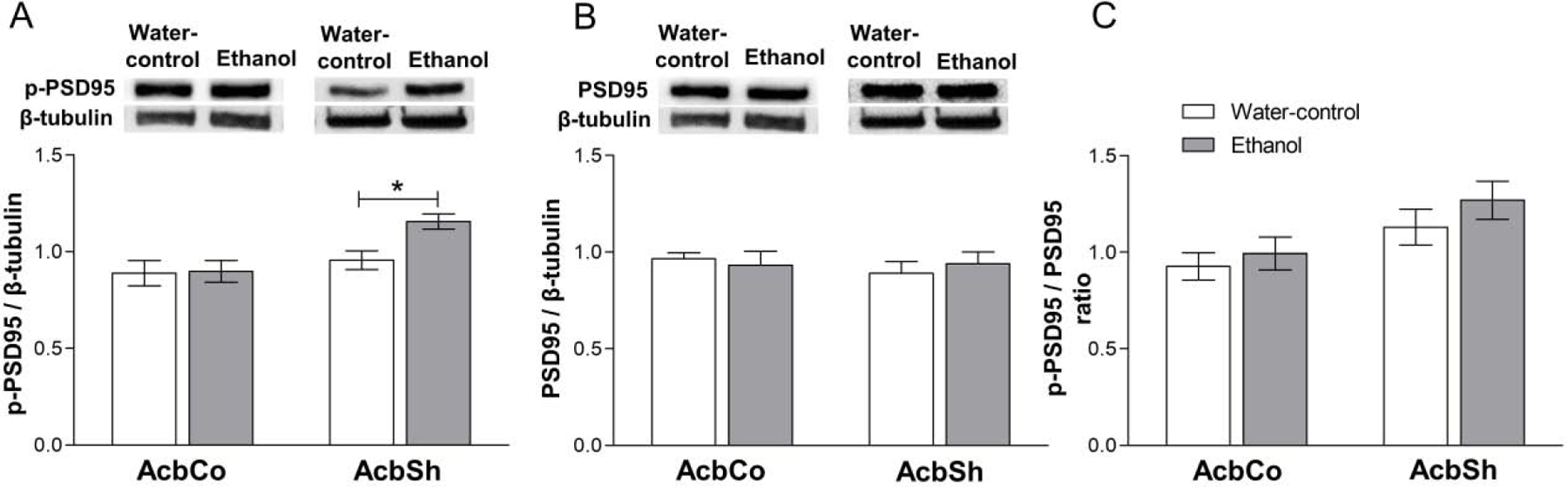
(A) Representative immunoblots for p-PSD-95 and β-tubulin in AcbCo and AcbSh respectively (upper panel) of the water-control and ethanol groups. Statistical analyses revealed no significant change in the p-PSD-95 protein expression within the AcbCo, whereas there was a significant upregulation of p-PSD-95 protein expression in the AcbSh (lower panel). (B) Representative immunoblots for PSD-95 and β-tubulin in the AcbCo and AcbSh respectively (upper panel) of the water-control and ethanol groups. Statistical analyses revealed no significant change in PSD-95 protein expression in either the AcbCo or AcbSh following ethanol drinking (lower panel). (C) Statistical analyses revealed no significant change in the p-PSD-95/PSD-95 ratio of the ethanol group compared to water-control group in either the AcbCo or AcbSh. The ratio is calculated by dividing the expression of p-PSD-95 by PSD-95 from the same western blot membranes. Data are shown as mean ± SEM; (*p < 0.05); (n = 8 for each group).
