Figure 6.
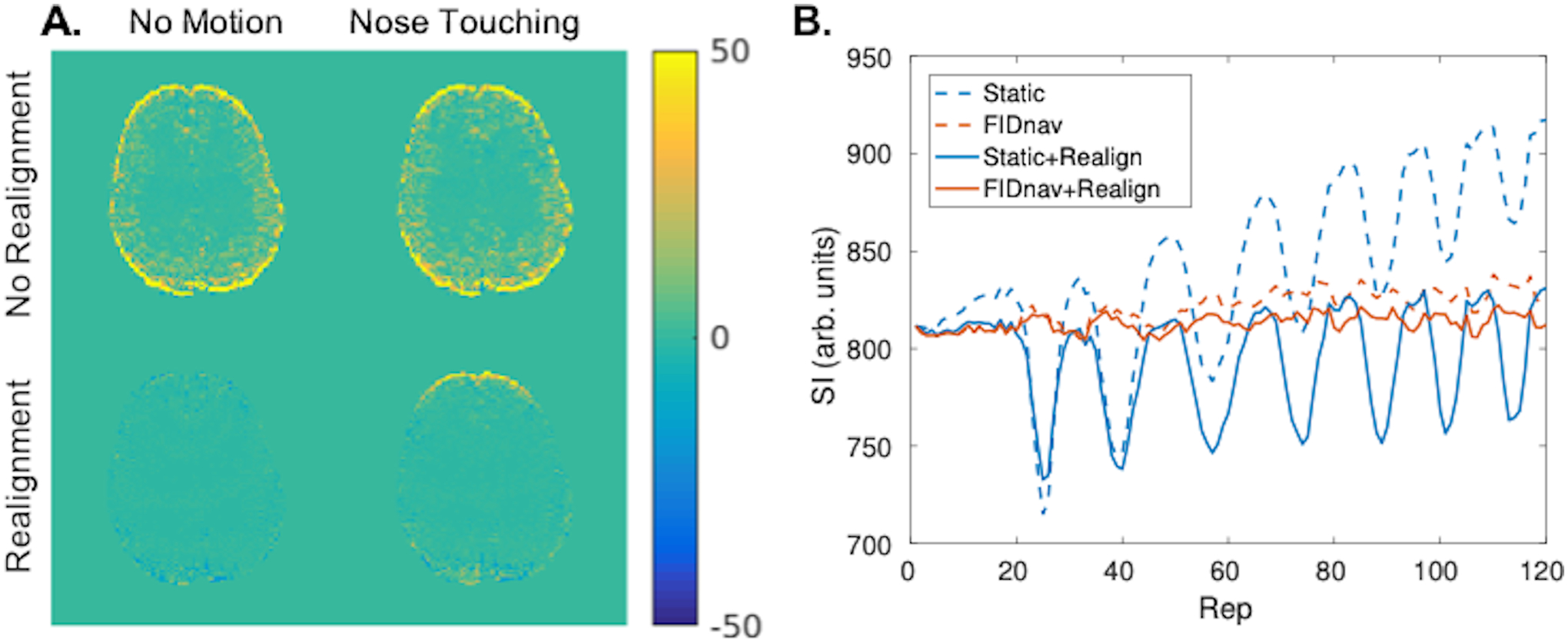
Maps showing difference in standard deviation (SD) between static distortion correction and FID-navigated distortion correction for no motion and nose touching paradigms, with and without rigid-body realignment (A). FIDnavs improved the SD of the raw image series by accounting for field changes over the course of the scan. Image realignment accounted for image drift due to global field changes; however, was insufficient to compensate for geometric distortions induced by nose touching in the frontal brain region. Signal within a ROI in the frontal brain region is shown for static and FIDnav-based distortion correction, with and without image realignment (B). FIDnav-based correction successfully removed signal fluctuations due to dynamically changing distortions.
