Extended Data Fig. 6 |.
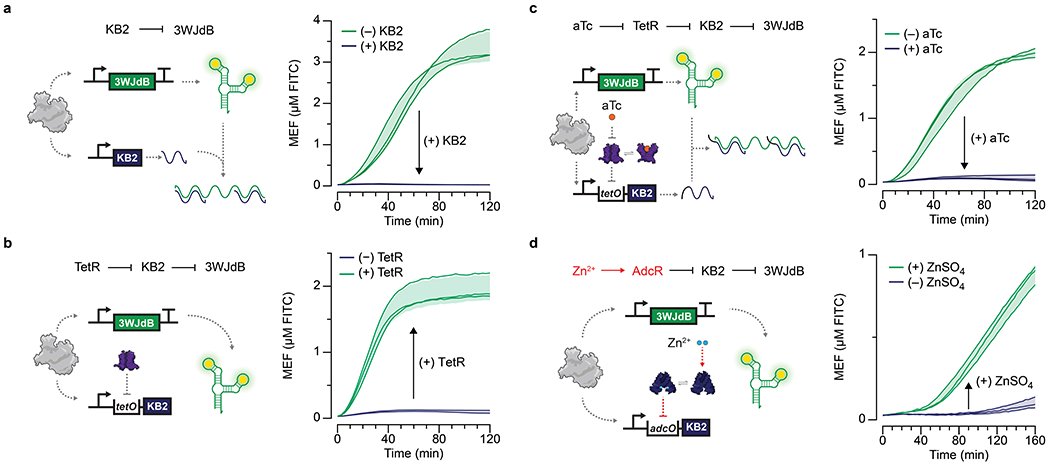
a, A kleptamer RNA (KB2) antisense to the dye-binding region of the broccoli aptamer can disrupt folding of 3WJdB and lead to the loss of fluorescence. Addition of a KB2-expressing template in a 4:1 ratio with the 3WJdB template inhibits signal. b, KB2 transcription can be regulated by TetR by placing the tetO site in between the T7 promoter and KB2 coding sequence. In the presence of 1.25 μM TetR dimer, the KB2 transcription is fully repressed, and the signal from 3WJdB is restored. c, Kleptamers can be used to invert the response of transcription factors when KB2 is regulated by TetR (1.25 μM dimer) and induced by aTc (2.5 μM shown). d, This scheme was used to create a ROSALIND zinc sensor with the aporepressor AdcR. When bound to Zn2+ (30 μM), AdcR (1.5 μM dimer) binds to its cognate operator sequence, adcO, placed upstream of the KB2 coding sequence, preventing KB2 expression and thereby activating fluorescence from 3WJdB. Arrows inside of the plots represent direction of regulation when indicated species are added. All data shown for n=3 independent biological replicates as lines with raw fluorescence values standardized to MEF (µM FITC). Shading indicates the average value of 3 independent biological replicates ± standard deviation. 3WJdB template concentrations used are: 25 nM for a-c and 7.5 nM for d. KB2 template concentrations used are: 100 nM for a, and 150 nM for b-d.
