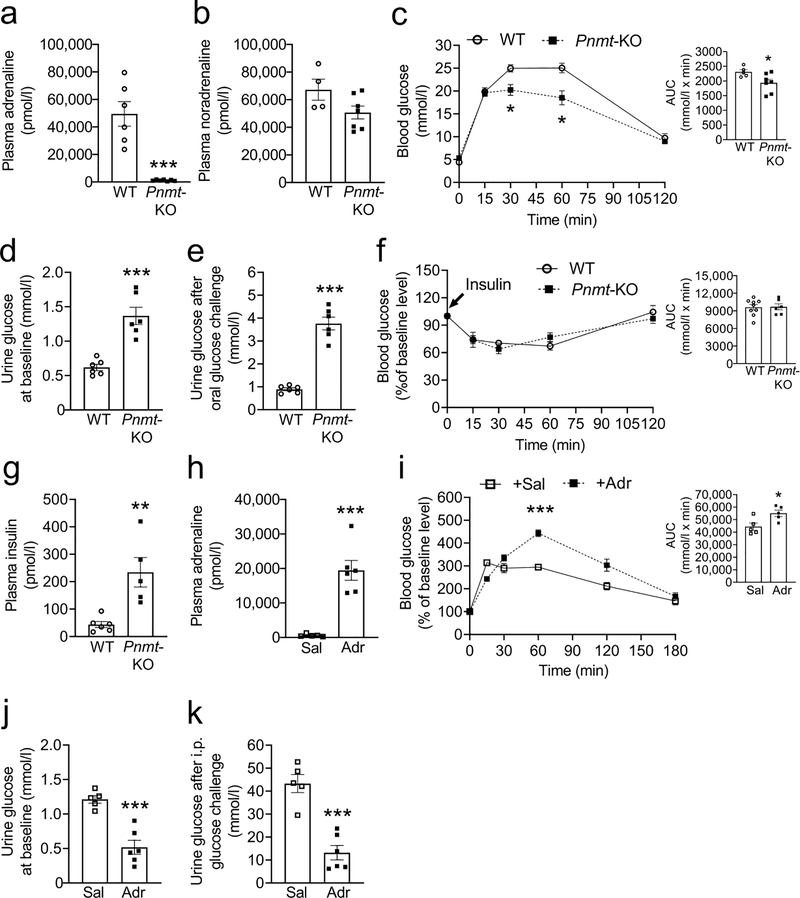
Fig. 6.
Blood and urine glucose levels in male 6- to 9-week-old-mice adrenaline-deficient (Pnmt-KO) mice before (a–g) and after (h–j) restoration of their plasma adrenaline levels. (a) Plasma adrenaline, (b) plasma noradrenaline, (c) OGTT, (d) 24 h urine glucose concentration at baseline, (e) 24 h urine glucose concentration after administering 250 mg glucose by oral gavage in adrenaline-deficient mice, (f) ITT, (g) plasma insulin levels in adrenaline-deficient mice, (h) plasma adrenaline (to validate its restoration), (i) OGTT, (j) 24 h urine glucose concentration at baseline and (k) 24 h urine glucose concentration after administering 100 mg glucose by i.p. injection, following restoration of plasma adrenaline in otherwise adrenaline-deficient mice. Bar graphs in (c), (f) and (i) represent the corresponding AUC. Two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test or repeated measures two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test were used for comparisons. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.. Error bars are mean ± SEM. Adr, adrenaline; Sal, saline