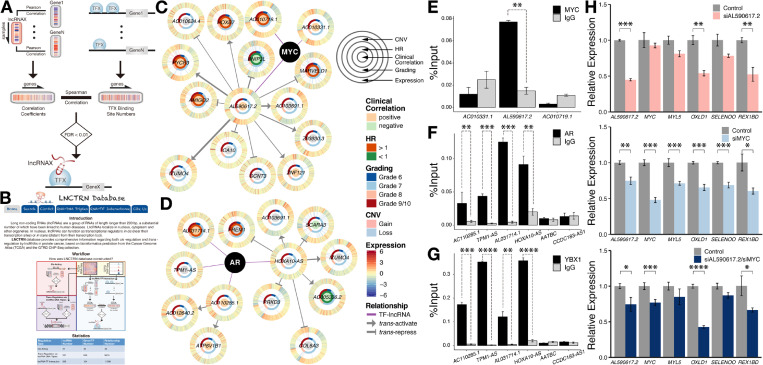
Fig. 7.
Long noncoding RNAs interacting with the prognostic signature constituent transcription factors. (a) Prediction pipeline of transcription factor interaction with lncRNAs by measuring the correlation between lncRNA regulation of gene expression and transcription factor occupancies in proximal regulatory regions among differentially expressed transcription factor targets. (b) The LNCTRN database provides comprehensive information of both cis- and trans-regulations by lncRNAs in prostate cancer. (c and d) A glance at the transcriptional network governed by the MYC– and AR–lncRNA interactions. Each gene is depicted as a multi-ring circle listing expression correlation (Pearson) with histologic grading, hazard ratio of disease recurrence, tumor grades, copy number variations, and zFPKM values from the inner to the outer layer. The outermost three datasets are plotted in the way that each “spoke” represents a single sample. Samples are arranged in the same order for all genes. (e) MYC-interacting lncRNAs displayed in (c) were validated by RIP-qPCR in LNCaP prostate cancer cells. (f) AR-interacting lncRNAs exhibited in (d) were validated by RIP-qPCR in LNCaP cells, in addition to their interactions with YBX1 (g). (h) Effects of AL590617.2 (siAL590617.2), MYC (siMYC), and AL590617.2/MYC (siAL590617.2/siMYC) knockdown on AL590617.2 and MYC candidate targets in LNCaP cells. * denotes p-value < .05; ** indicates p-value < .01; *** signifies p-value < .001; **** represents p-value < .0001.