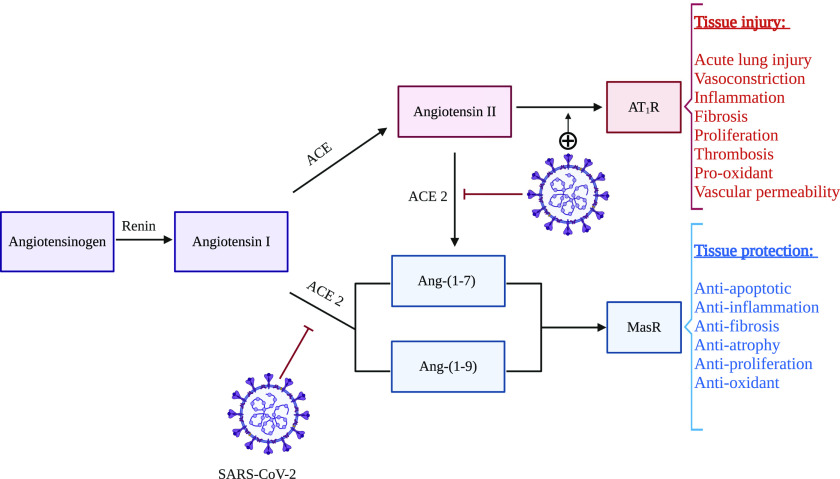
Fig. 1.
Possible interactions between SARS-CoV-2 and the renin angiotensin system: SARS-CoV-2 binds to cell surface ACE2 receptor with its spike protein for host cell entry. After endocytosis of the virus, surface ACE2 is downregulated but ACE remains unchanged. This event alters the balance of the RAS. Ang-II is increased and the injurious effects of this hormone (vasoconstriction, inflammation, fibrosis etc.), mediated by AT1R, can result in excessive tissue damage, e.g., lung tissue damage. On the other hand, the concomitant decrease in Ang-(1–7) and Ang-(1–9) hinders the protective effects (antiapoptotic, anti-inflammation, antifibrosis etc.) of these hormones, mediated by Mas receptor (MasR), causing further tissue injury.