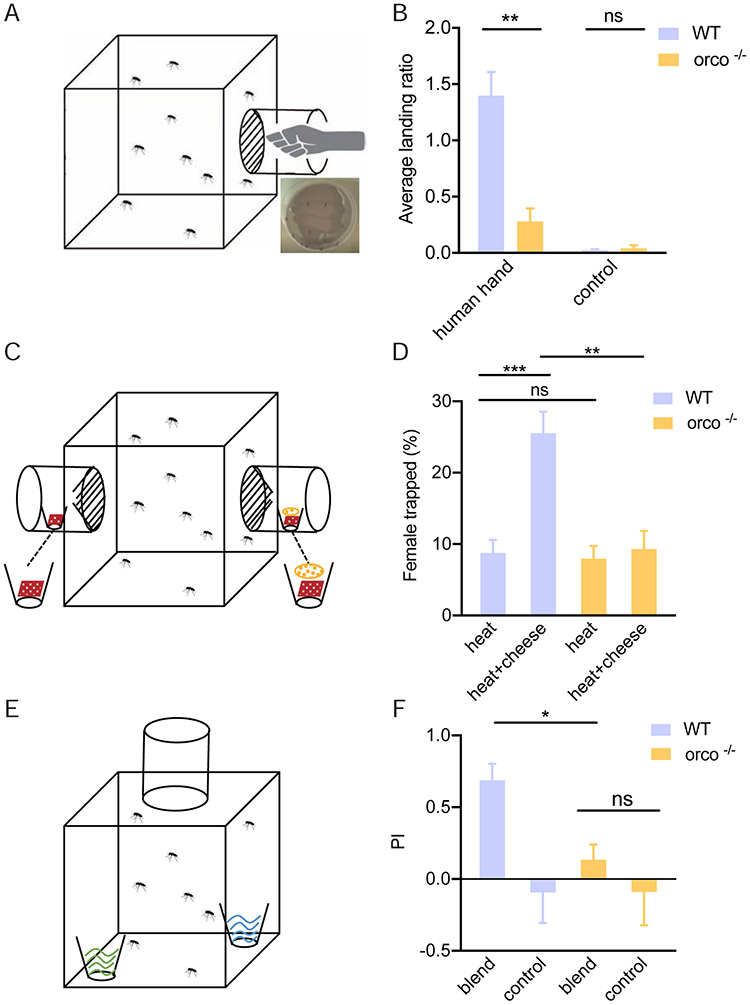
Figure 6.
Behavioral responses of wild-type and orco−/− mosquito to human- and non-human-derived odors: (A) Schematic graphic of the setup of human hand proximity bioassay; (B) Comparison of wild-type and orco−/− mosquito hand attraction (n=7-11); (C) Schematic representation of the setup of the Limburger cheese human foot mimic bioassay; (D) Comparison of the wildtype and orco−/− mosquito attraction to Limburger cheese to (n=6); (E) Schematic graphic of the setup of oviposition preference assay; (F) Comparison of attraction of gravid wild-type and orco−/− female mosquitoes to the oviposition blend (n=5). Nonparametric Mann-Whitney test was applied in the statistical analysis, with p<0.05 (*), p<0.01 (**) and p<0.001 (***) indicating significant differences.