Figure 1.
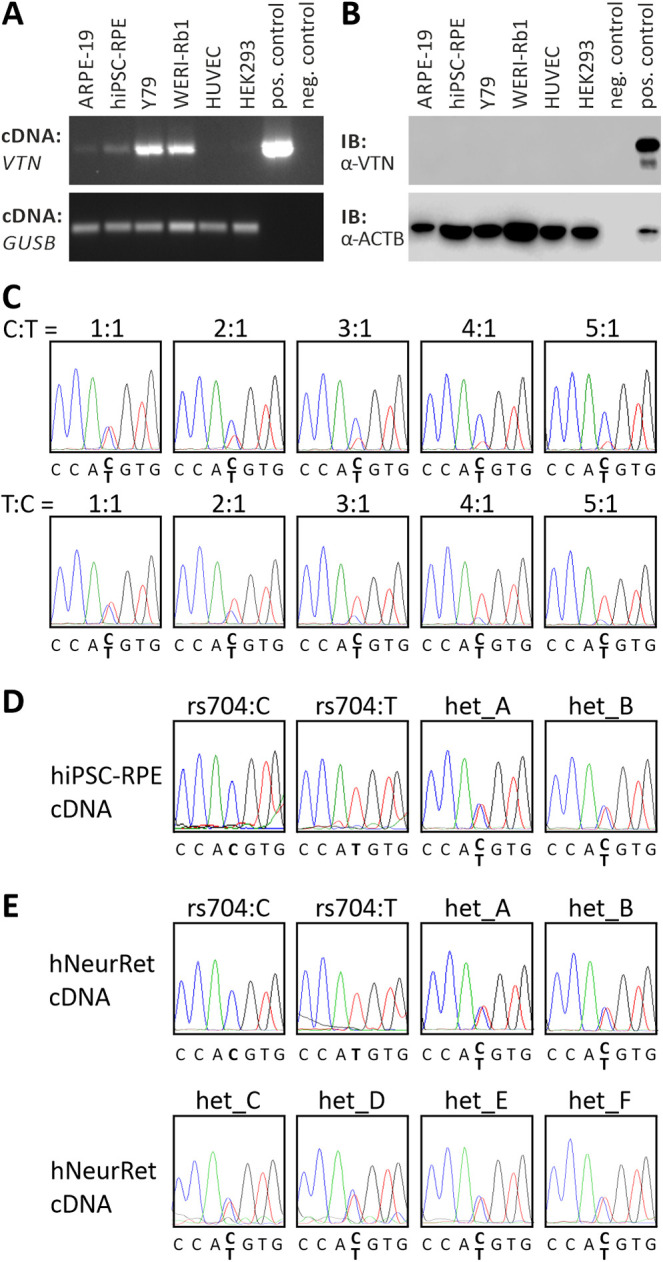
Endogenous vitronectin expression in retinal and non-retinal cell lines. (A) RT-PCR analysis of VTN gene expression in ARPE-19, hiPSC–RPE, Y79, WERI-Rb1, HUVEC, and HEK293 cells. Expression vectors containing cDNA of non-AMD-risk-associated VTN served as positive control; no template was added to the negative control. GUSB gene expression was assessed as control for RNA integrity. (B) Western blot analysis of vitronectin protein expression in ARPE-19, hiPSC–RPE, Y79, WERI-Rb1, HUVEC, and HEK293 cells. HEK293 cells transfected with expression vectors for VTN_rs704:C served as positive control. Cell lysates were subjected to western blot analyses using antibodies against vitronectin. The ACTB immunoblot was performed as loading control. (C) Titration series with recombinant VTN cDNA isoforms derived from the non-risk (rs704:C) or the risk (rs704:T) haplotype (ratio of C:T allele given in the figure). Isoforms were determined by sequence analysis. VTN_rs704:C and VTN_rs704:T transcription in hiPSC–RPE cells (D) or human retinal tissues (E) of different donors was analyzed by semi-quantitative sequencing of allele-specific transcripts. Non-AMD-risk-associated and AMD-risk-associated alleles at the vitronectin gene locus were determined by genomic sequencing of variant rs704 (see Supplementary Fig. S4). Expression of the non-AMD-risk-associated and AMD-risk-associated VTN mRNA isoforms was investigated by cDNA sequencing of variant rs704.
