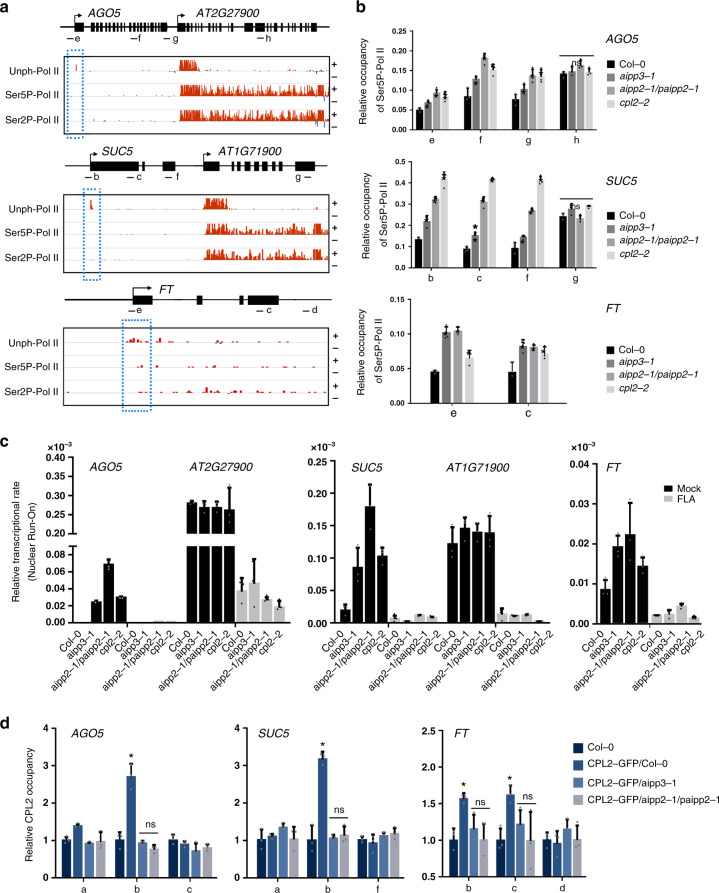
Fig. 7. BPC complex directly connects H3K27me3 recognition with transcriptional repression.
a Snapshots showing the occupancies of different Pol II forms on selected target genes using a published Pol II NET-seq database. The red and blue lines indicate the Pol II signals in the plus and minus strands, respectively. The dashed red boxes indicate the occupancies of Pol II on the selected target genes. The black arrows indicate the transcriptional direction. b The ChIP-qPCR validation of the occupancy of Ser5P-Pol II on selected genes in different mutants. The lowercase letters the examined regions (the same below). The occupancy was normalized to the ACT7. The data are the means ± S.D. of three biological repeats. Unpaired one-tailed t test was performed and *p value < 0.01. ns no significance. c Nuclear run-on analysis showing the relative Pol II transcription rate at the selected target genes in Col-0 and bpc mutants with or without FLA treatment (mock). AT2G27900 and AT1G71900 genes serve as control genes. The relative transcription rate was normalized to 18 S rRNA. The data are the means ± S.D. of three biological repeats. d CPL2 ChIP-qPCR results showing the relative occupancy of CPL2 at selected target genes in the presence and absence of AIPP3 and AIPP2/PAIPP2. The occupancy was first normalized to AtSN1 and then normalized to Col-0. The data are the means ± S.D. of three biological repeats. Unpaired one-tailed t test was performed and *p value < 0.01.