Fig 2.
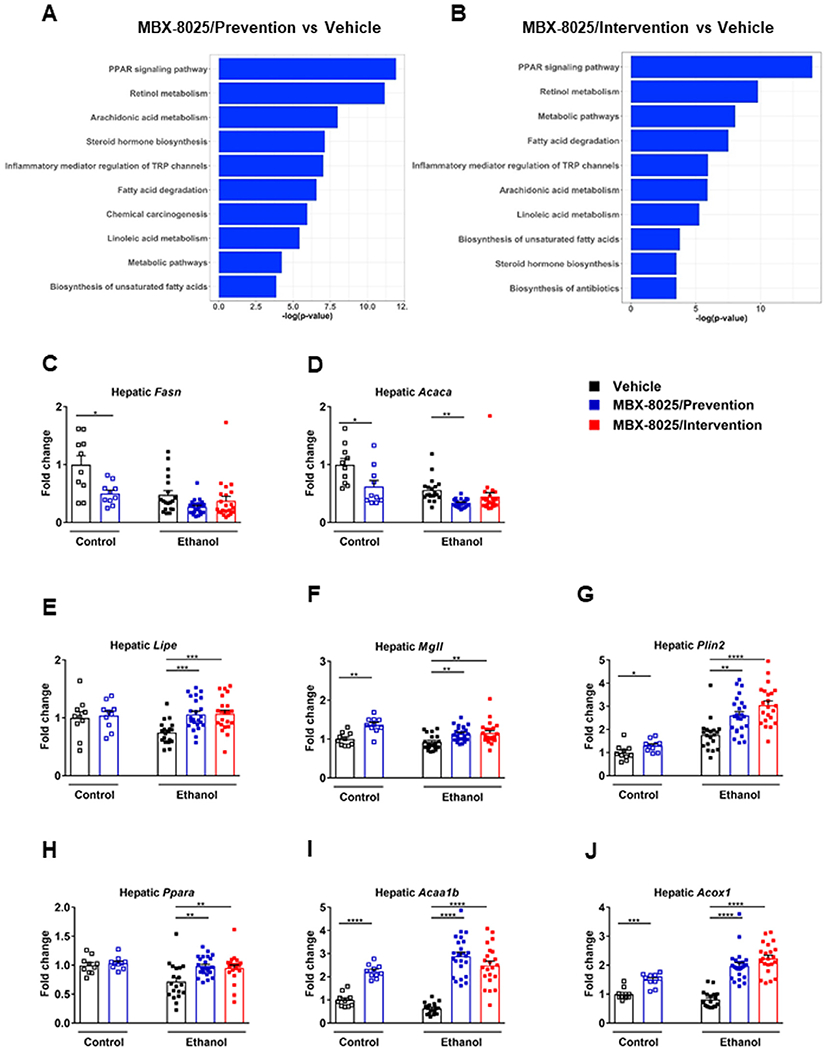
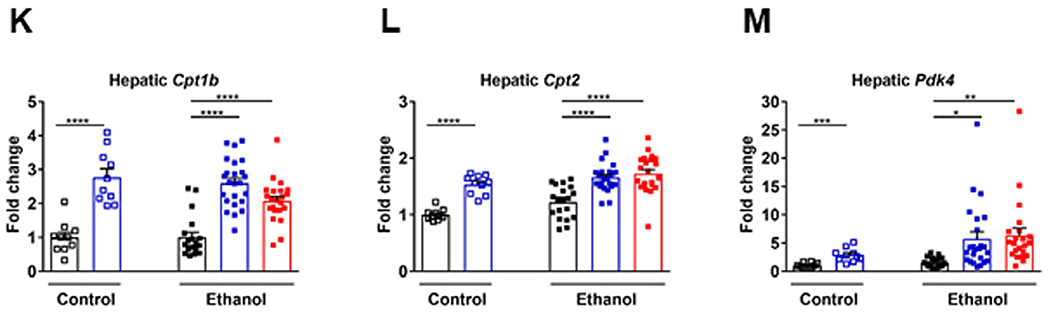
Effect of MBX-8025 on hepatic gene expression. C57BL/6 mice were fed an oral isocaloric (control) diet (1-2 technical replicates) or a chronic Lieber-DeCarli diet for 8 weeks followed by 1 binge of ethanol (3–4 technical replicates), and treated with vehicle, or MBX-8025 (10 mg/kg/d) daily by adding MBX-8025 in the liquid diet during the entire feeding period (prevention) or during the last 4 weeks of ethanol feeding (intervention). (A) Ranking of top 10 biological processes by −log(P value) in the liver of MBX-8025 treated (prevention group) compared with vehicle treated, ethanol-fed mice. (B) Ranking of top 10 biological processes by −log(P value) in the liver of MBX-8025 treated (intervention group) compared with vehicle treated, ethanol-fed mice. (C) Hepatic levels of Fasn mRNA. (D) Hepatic levels of Acaca mRNA. (E) Hepatic levels of Lipe mRNA. (F) Hepatic levels of Mgll mRNA. (G) Hepatic levels of Plin2 mRNA. (H) Hepatic levels of Ppara mRNA. (I) Hepatic levels of Acaa1b mRNA. (J) Hepatic levels of Acox1 mRNA. (K) Hepatic levels of Cpt1b mRNA. (L) Hepatic levels of Cpt2 mRNA. (M) Hepatic levels of Pdk4 mRNA. Control diet: Vehicle, n = 10; MBX-8025/Prevention, n = 10; Ethanol diet: Vehicle, n = 19; MBX-8025/Prevention, n = 24; MBX-8025/Intervention, n = 22. Results are expressed as mean § s.e.m. (C-M). P values were determined using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test for ethanol-fed mouse groups and Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon test for control diet-fed mouse groups (C-M). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.
