Figure 6. In silico analysis of REN variants.
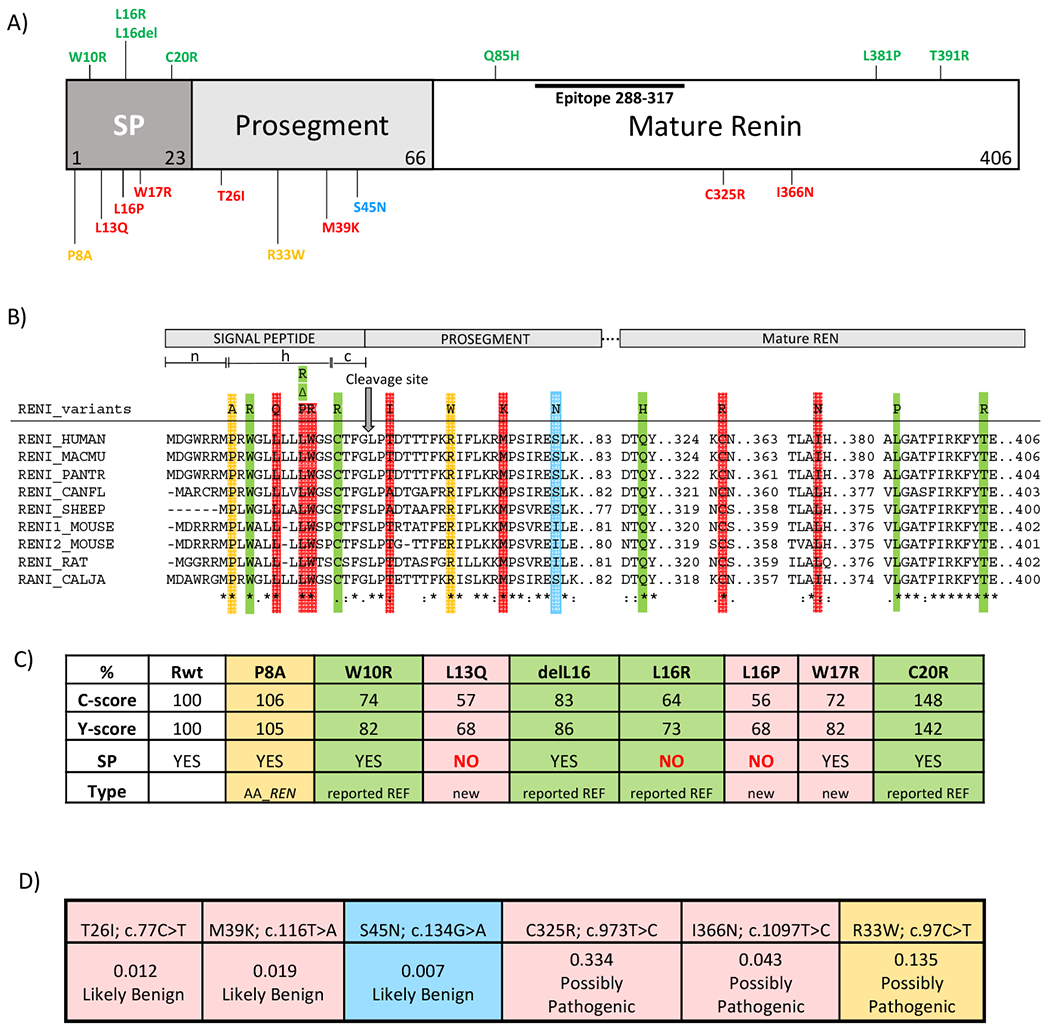
(A) Preprorenin, a precursor of prorenin and renin, consists of : i) the signal peptide (SP) essential for targeting and insertion of the synthesized protein into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane, ii) the prosegment that determines the biosynthesis, cellular trafficking and enzymatic activity and iii) the mature enzymatically active renin that is formed upon the proteolytic cleavage of prorenin. Novel pathogenic mutations identified and characterized in this study are shown in red. Previously reported dominant mutations associated with ADTKD are shown in green. The p.S45N is considered nonpathogenic and is shown in blue. Variants of unknown significance identified in African-American variants are shown in yellow. Epitope 288-377 denotes the protein segment recognized by the anti-preprorenin antibody used in this study. The n, h and c regions respectively denote stretches of positively charged amino acids (n-region), hydrophobic amino acids (h-region) essential for targeting and insertion of the signal peptide into ER membrane, and polar amino acids (c-region), forming a recognition site for the signal peptidase that releases translocated preproprotein from its ER membrane-anchored signal peptide. (B) Amino acids conservation across mutated segments of REN in higher mammals. Asterisks (*) indicate amino acid residues that are absolutely conserved, a colon (:) indicates residues with strong conservation and a dot (.) indicate residues with weak conservation between species. (C) Computational prediction by the SignalP 4.1 server of the impact of missense REN mutations located in the signal peptide on the conformation of the signal peptide cleavage site location (C-score) and on the sequence characteristics of the signal peptide (Y-score). SP denotes presence (YES/NO) of the signal peptidase cleavage site within the given sequence. The first 60 N-terminal amino acids of REN were used for this calculation. (D) Computational prediction by Mendelian Clinically Applicable Pathogenicity Score (M-CAP) of the pathogenicity of missense REN mutations located in the propeptide and mature renin.
