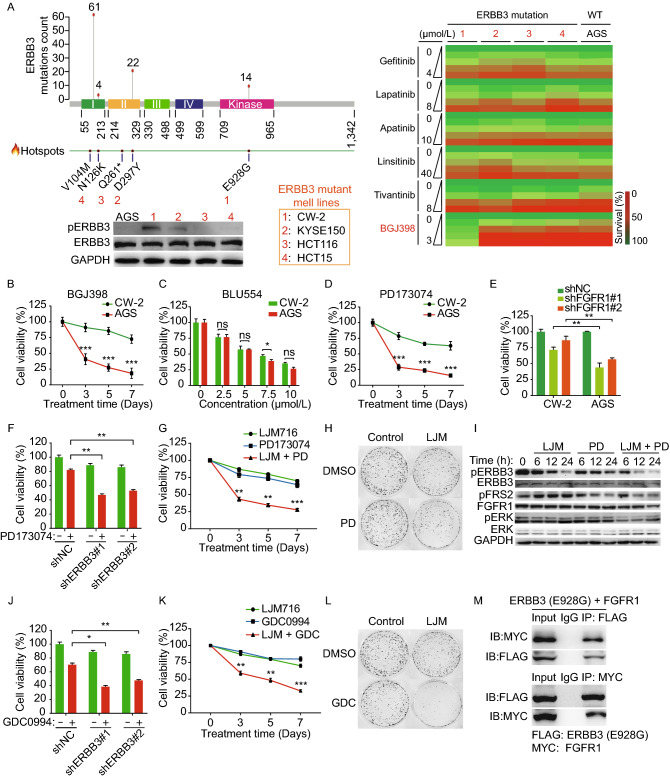
Figure 1.
Identification of ERBB3 kinase domain mutant E928G contributes to resistance of GI cancer cells to FGFR1 inhibition via downstream MEK-ERK signaling pathway. (A) A functional screen of TKIs sensitivity was performed in 5 selected GI cancer cell lines, which closely recapitulate the spectrum of ERBB3 mutation across 1165 human cancer samples (Cancer Hotspots Database, https://www.cancerhotspots.org). On the top of the left panel: the numbers below the figure refer to amino acid positions, and the hotspot mutation sites are shown as solid red circles. A total of 214 ERBB3 mutations were identified in 1,165 cancer samples, and the three most prevalent hotspots (V104, D297, and E928) are shown, with the number of samples indicated. On the bottom of the left panel: protein levels of pERBB3 and ERBB3 in 5 selected GI cancer cell lines measured by Western blot. GAPDH serves as a loading control. The right panel: heat map shows the screening results of six TKIs in a subset of five separate GI cancer cell lines with various ERBB3 mutations (AGS cells express wild-type ERBB3). Cells were treated with the indicated TKIs at the indicated concentrations, and cell viability was measured after 72 h. (B) CW-2 and AGS cells were treated with 2 μmol/L BGJ398, and cell viability was measured on day 0, 3, 5, and 7. (C) Cell viability of CW-2 and AGS cells treated for 3 days with the FGFR4 inhibitor BLU554 at the indicated concentrations. (D) Cell viability of CW-2 and AGS cells treated with 3 μmol/L PD173074 for 7 days. (E) Cell viability of CW-2 and AGS cells infected with a control shRNA lentivirus construct (shNC) or two different anti-FGFR1 shRNA constructs. (F) Cell viability was measured in CW-2 cells transfected with the indicated shRNA construct and then treated for 3 days with or without 3 μmol/L PD173074. (G) Time course of cell viability of CW-2 cells treated with either 10 μg/mL LJM716 alone, 3 μmol/L PD173074 alone or both LJM716 and PD173074. (H) Foci formation was measured for CW-2 cells treated for 2 weeks with DMSO (control), 10 μg/mL LJM716, 2 μmol/L BGJ398, or both LJM716 and BGJ398. (I) CW-2 cells were treated with relative high dose of LJM716 (20 μg/mL), PD173074 (10 μmol/L), or both, followed by western blot analyses at the indicated time. (J) Cell viability was measured in CW-2 cells subjected to shRNA-mediated ERBB3 knockdown followed by 3 days of treatment with 10 μmol/L GDC0994. (K) Time course of cell viability of CW-2 cells treated with either 10 μg/mL LJM716 alone, 10 μmol/L GDC0994 alone or both LJM716 and GDC0994. (L) 2 weeks foci formation was measured for CW-2 cells treated with DMSO (control), 10 μg/mL LJM716, 10 μmol/L GDC0994, or both LJM716 and BGJ398. (M) HEK293T cells were co-transfected with FLAG-tagged ERBB3-E928G and MYC-tagged FGFR1, 3 days after transfection, cell lysates were subjected to Co-IP using anti-FLAG and anti-MYC antibodies. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ns, not significant