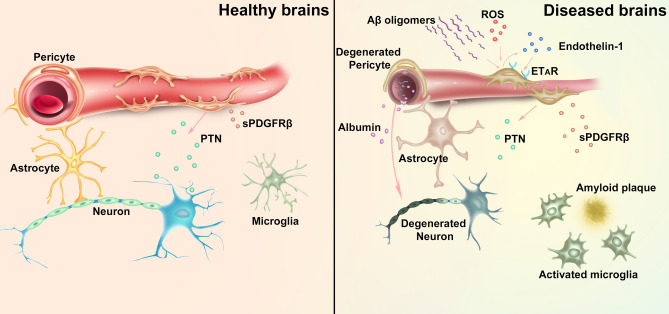
Fig. 1.
Schematic of the roles of pericytes in neurovascular interactions in healthy and diseased brains. Left: in the healthy brain, pericytes maintain the integrity of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and regulate cerebral blood flow. Pericytes secrete pleiotrophin (PTN) to support neuronal growth. Right: in Alzheimer’s disease, Aβ oligomers stimulate ROS generation and endothelin-1 release (possibly from pericytes), which in turn activates pericyte ETA receptors (ETAR), leading to capillary constriction and cerebral blood flow reduction. Degeneration of pericytes causes BBB breakdown, plasma leakage, and deprivation of PTN, which result in neurodegeneration. An increase of pericyte-derived soluble PDGFRβ (sPDGFRβ) in the CSF is also associated with early cognitive impairment and BBB breakdown.