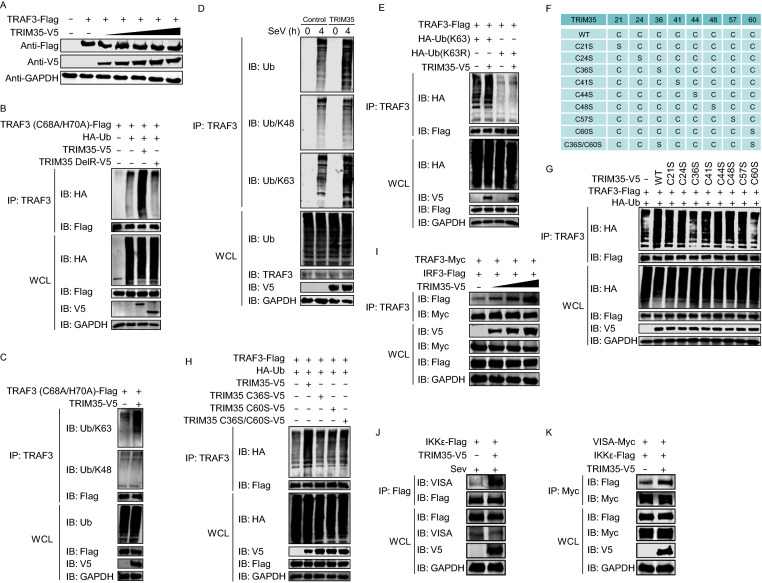
Figure 5.
TRIM35 promotes K63-linked polyubiquitination of TRAF3. (A) IB analysis of HEK293T cells expressing TRAF3-Flag and increasing amounts of TRIM35-V5. (B) Co-IP and IB analysis to assess TRAF3 ubiquitination in HEK293T cells expressing TRAF3 (C68A/H70A)-Flag, HA-ubiquitin, with or without V5-tagged TRIM35 or its DelRING mutant. (C) Co-IP and IB analysis to assess TRAF3 ubiquitination in HEK293T cells expressing TRAF3 (C68A/H70A)-Flag, with or without TRIM35-V5. (D) Co-IP and IB analysis to assess endogenous TRAF3 ubiquitination in stable TRIM35-overexpressing or control THP-1 cells infected with SeV at the indicated timepoints. (E) Co-IP and IB analysis to assess TRAF3 ubiquitination in HEK293T cells expressing TRAF3-Flag, with or without TRIM35-V5, HA-ubiquitin (K63), and HA-ubiquitin (K63R). (F) Mutants of human TRIM35 in which different cysteine residues were replaced. (G and H) Co-IP and IB analysis to assess TRAF3 ubiquitination in HEK293T cells expressing TRAF3-Flag, HA-ubiquitin, and V5-tagged TRIM35 or its mutants as in (F). (I) Co-IP and IB analysis of HEK293T cells expressing TRAF3-Myc, IRF3-Flag, along with increasing amounts of TRIM35-V5. (J) Co-IP and IB analysis of HEK293T cells expressing IKKε-Flag, with or without TRIM35-V5, followed by infection with SeV for 12 h. (K) Co-IP and IB analysis of HEK293T cells expressing IKKε-Flag, VISA-Myc, with or without TRIM35-V5. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments