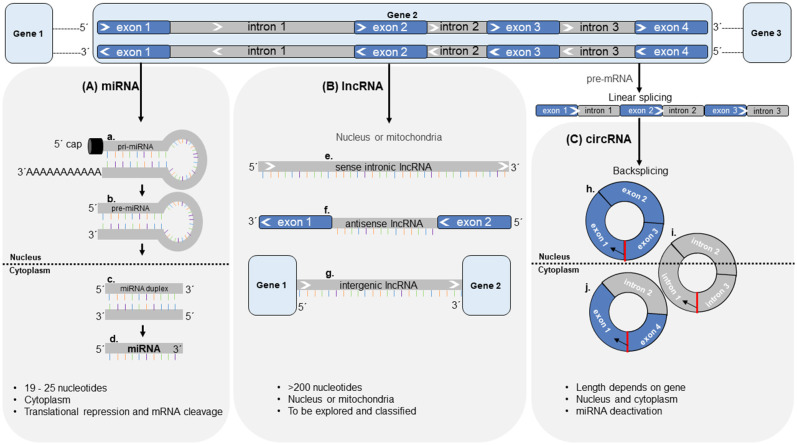
Figure 4.
Synthesis, length, cellular location and molecular function of non-coding RNAs. (A) miRNAs are expressed from miRNA genes. Located in the nucleus, pri-miRNAs (a) are transcribed from the DNA and are processed by Drosha-Pasha processing complexes giving rise to pre-miRNAs (b). Pre-miRNAs are translocated from the nucleus into the cytoplasm via Exportin-5, where they are further processed by Dicer enzyme to form miRNA duplex (c) and later the final miRNA (d). (B) lncRNAs arise from sense and antisense strands of introns (e), exons (f), and intergenic regions (g) of the DNA and are located within the nucleus or mitochondria. (C) circRNAs are generated from the pre-mRNA in a process called back-splicing' resulting in circRNAs made up of either exon-exon junctions (h), intron-intron junctions (i) or exon-intron junctions (j). Red indicates the back-splice junction. Black arrows indicate direction of back-splicing in circRNAs. circRNA = circular RNA, lncRNA = long non-coding RNA, miRNA = microRNA, mRNA = messenger RNA.