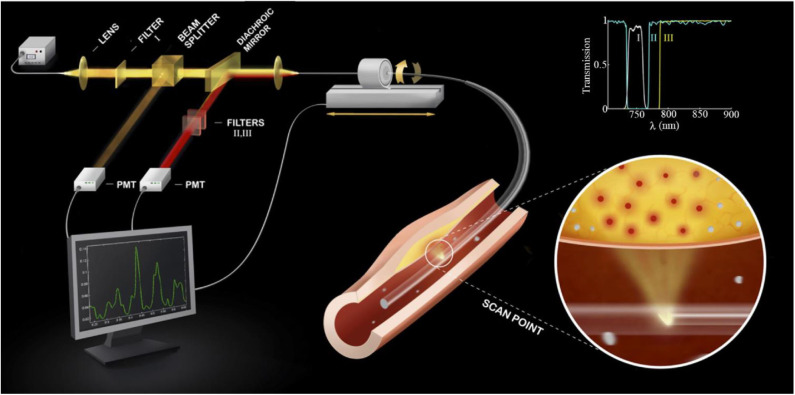
Figure 2.
Diagram of a first-generation standalone 2D NIRF Imaging System. The tip of the probe contains a right angle coated prism that focuses laser light into the artery wall, activating fluorophores to their excited state to allow fluorescence emission. Subsequently, fluorophores will emit longer wavelength (lower energy) fluorescent light back into the optical fiber. The fluorescent light is then directed to a dichroic beam splitter that selectively directs it into a photomultiplier tube. The beam passes additional filters to minimize the parasitic signals of laser photons and autofluorescence. The inset shows the spectra of the three filters (I, II, III) used in the system. 2D, 2-dimensional; NIRF, near-infrared fluorescence. Jaffer et al. (13), by permission of American College of Cardiology. License number: 4720261188070.