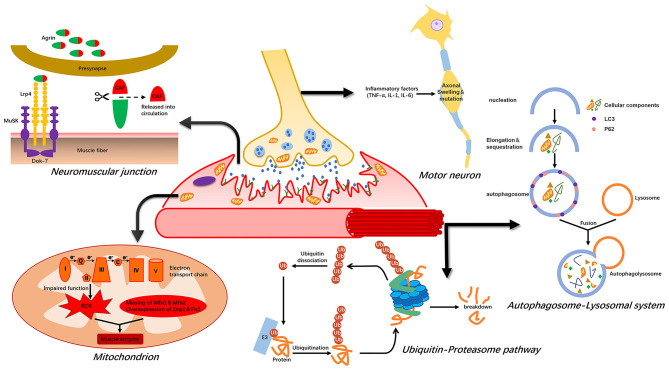
Figure 1.
Possible mechanism of intensive care unit-acquired weakness (ICU-AW). Muscle atrophy is caused by an imbalance between protein synthesis and degradation. The ubiquitin–proteasome pathway and autophagy–lysosome system are activated during this period, leading to massive degradation of muscle proteins. ROS released after mitochondrial damage also induce proteolysis. The agrin-MuSK-Lrp4 signaling pathway is impaired during abnormal NMJ function, leading to muscle atrophy. Finally, inflammatory factors can cause axonal swelling in motor neurons, resulting in neurapraxia.